What We Know (and Don’t) About the Oil Spill in Orange County
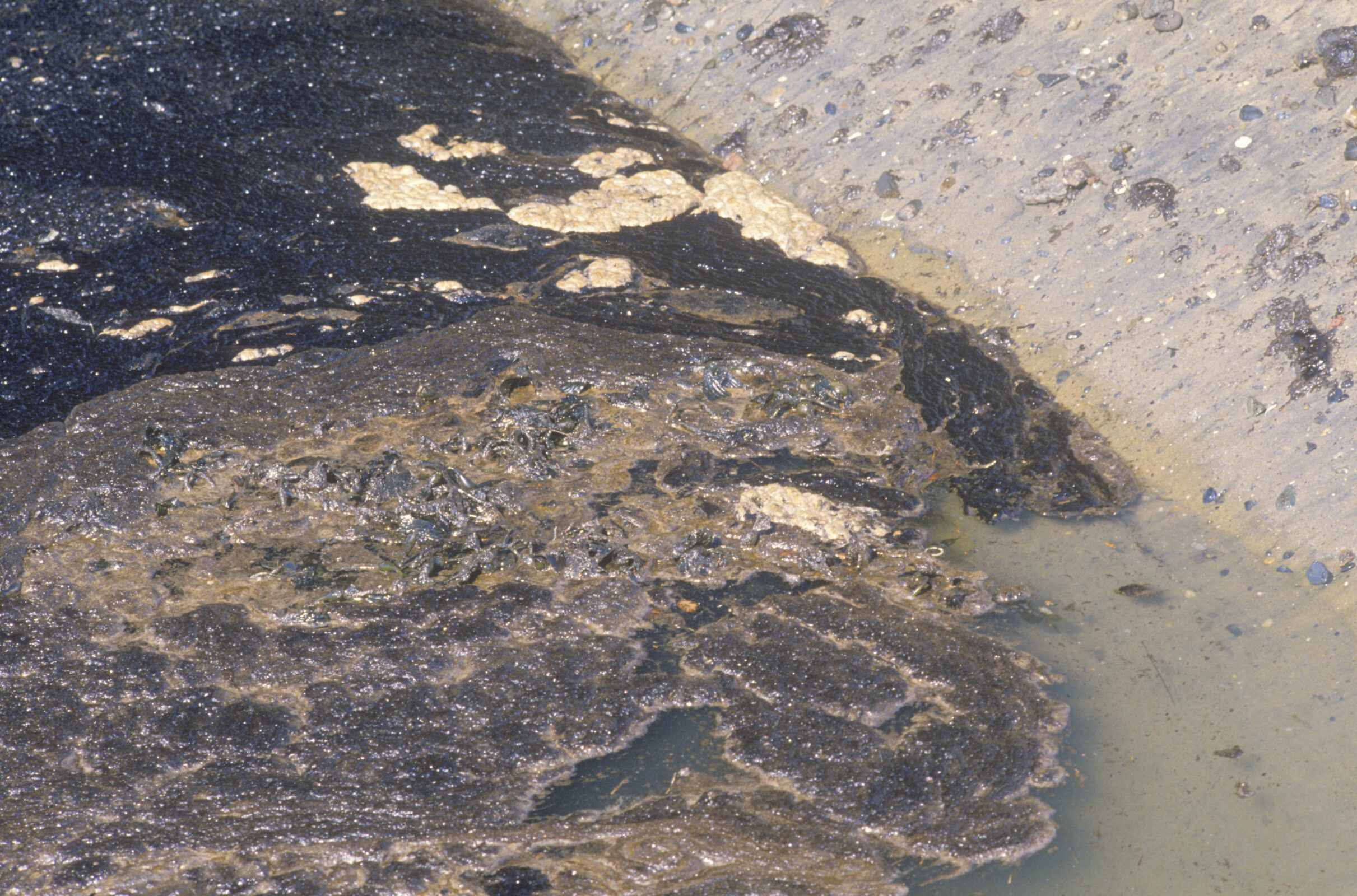

We are heartbroken and outraged. Crude oil spilled from a pipe into the ocean near Huntington Beach, Orange County in October 2021. Here’s how to take action. This oil spill has taken place in unceded Acjachemen and Tongva ancestral waters.
LATEST UPDATE as of 2/8/22
The government agencies responding to the oil spill announced last week that their cleanup operations have ended for the two ruptured pipelines off the coast of Huntington Beach. All coastal habitats are deemed to be clean of oil, and the phone number and email address for reporting tarballs have been disabled. The public has been advised to contact the National Response Center (1-800-424-8802) if more oil is observed on the beach or in the water.
While the cleanup has concluded, the response to the oil spill is far from over. The California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW) will now complete a Natural Resource Damage Assessment (NRDA). The NRDA will financially quantify the damage done by the oil spill in terms of habitat and human usage. The assessment has required that Amplify Energy pay that amount in restitution. The CDFW will need to conduct multiple scientific studies to collect and analyze a large volume of environmental data, so expect the NRDA to take several years to finalize.
We will not know the full environmental impact of the oil spill until the NRDA concludes, but we do have some preliminary details. The first ruptured pipeline released 25,000 gallons of oil into the ocean, and cleanup crews managed to remove 9,076 gallons. That means over half the oil that was spilled remains in the ocean or on the beach. In addition, the oil that was recovered may have harmed wildlife before being cleaned up. In total, 124 animals (birds, mammals, herptiles) were found to be oiled, and only 36 survived. The second ruptured pipeline released less oil into the ocean, but there is currently no estimate for how many gallons. Cleanup crews for the second pipeline recovered 176-236 gallons of oil from the ocean, and no oiled wildlife was observed.
Both pipelines have been emptied, and they are no longer in operation. However, the pipeline operators appear to be intent on repairing the pipelines and using them in the future. The Pipeline Hazardous Materials Safety Administration is reviewing permanent repair plans for the pipelines. Please direct any questions about this process to phmsa.publicaffairs@dot.gov.
LATEST UPDATE as of 1/11/22
The agencies tasked with responding to the oil spill (U.S. Coast Guard, California Department of Fish & Wildlife, Orange County, and San Diego County), have ended their cleanup operations at all Orange County and San Diego County beaches. Tragically, a rupture was discovered in a separate but nearby pipeline on January 2, 2022. Crews were deployed to clean up the oil sheen, and protective booms were placed at the entrances to Orange County wetlands to absorb any floating oil. It is reported that no oil from the second pipeline rupture has reached the beaches. At this time, no fisheries closures have been recommended by the Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment.
The breach points in both pipelines have been identified and are being repaired. The remaining oil in the pipelines will be evacuated once repairs are completed. Cleanup crews will remain on call for an undetermined amount of time to respond to new incidents of oil sheens or tar balls. Oil and tar ball sightings should be reported to the National Response Center (1-800-424-8802) and California Office of Emergency Services (1-800-852-7550). For additional information about the oil spill, email ocoilspillinv@gmail.com
LATEST UPDATE as of 12/17/21
Texas Company Indicted for Orange County Oil Spill Devastation
LATEST UPDATE as of 12/1/21
It has now been nearly 9 weeks since the Orange County oil spill.
After the Orange County Oil spill released over 25,000 gallons of oil in early October, the Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment (OEHHA) recommended the closure of both commercial and recreational fishing to the California Department of Fish and Wildlife. The recommendation suggested a moratorium that would encompass the area from Huntington Beach to Dana Point. As of October 3rd, the closure prohibited the take of all fish and shellfish from an area that included over 20 miles of California coastline, with the boundary reaching 6 miles out to sea. The OEHHA had identified “that the threat to public health from consuming fish in the affected area was likely” and a few days after the original closure began, the CDFW expanded the prohibited territory to include bays and harbors from Seal Beach to San Onofre State Beach.
From October 14 to November 3, the OEHHA sampled seafood along this 650 square mile area to measure and evaluate polyaromatic hydrocarbon levels. PAHs are harmful chemicals found in oil and can accumulate along marine food chains, specifically in fish and shellfish caught for human consumption, “causing increased risk to cancer and other adverse health conditions.”
Three days ago, after extensive testing, the OEHHA announced that as of November 29, “there is no further risk to public health from seafood consumption in the affected area.” Following the OEHHA recommendation, Director Bonham of the CDFW signed a declaration lifting the ban on fisheries allowing fishing to resume no later than midday on November 30, 2021.
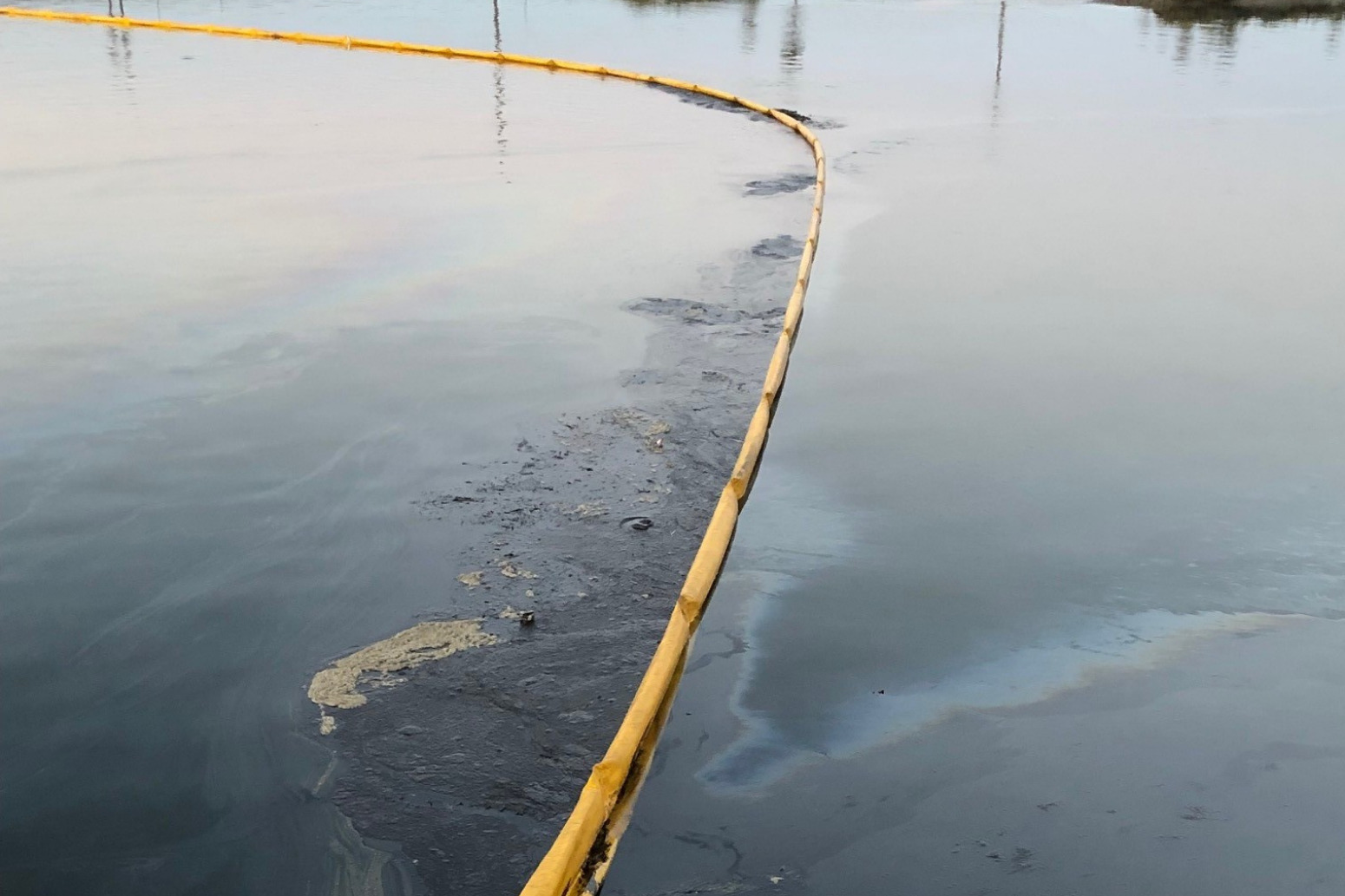
Beach and shoreline cleanup activities in Orange and Sand Diego counties are winding down as most beaches impacted by the spill have been deemed clear of oil by the spill response agencies (see here for how they determine this). There are still two segments of coastline in Orange County and three in San Diego County where there are ongoing cleanup activities. The US Coast Guard and Office of Spill Prevention and Response will respond to any new reports of oil on the coastline even at beaches where cleanup operations have ceased.
LATEST UPDATE as of 10/29/21
It has now been nearly 3 weeks since the Orange County oil spill.
Monitoring and cleanup continues by the Unified Command. More than 5,000 gallons of oil have been recovered by skimmers and over half a million pounds of oily sand and debris have been removed thus far. Based on a recently released water quality report, there appears to be very little detectable toxins in the water and all beaches and harbors are now open. Heal the Bay strongly believes that more monitoring is needed for the affected area and we encourage all beachgoers to continue checking the Beach Report Card before heading to the water.
The Talbert Marsh still has floating barriers in place, but all other barriers have now been removed. Boat decontamination stations are available in harbors and all affected boats can be cleaned at the expense of the responsible party. The oiled wildlife that were recovered alive are doing well, and fewer in number than originally feared. Of the 33 oiled birds recovered alive, 20 have already been released. The total number of animals affected is just under 100 and includes birds, marine mammals, and fish.
Tar balls still may occur on beaches, and can be reported to CDFW at tarballreports@wildlife.ca.gov. Questions still remain about when and how the damage to the pipeline occurred, the exact amount of oil spilled, when and how the response began and how effective that response has been in properly informing and protecting the public. It does appear that less oil was spilled than the first estimates, and the minimum estimate is now just over 25,000 gallons in total.
Keep following Heal the Bay and the official Southern California Spill Response page for more updates.
Update as of 10/14/21
Orange County beaches are open, but please be cautious.
Orange County officials re-opened all beaches on Monday, October 11 after a week-long closure due to the oil spill. The decision to open the beaches appears to be based on a water quality report recently conducted by a third-party contractor. They collected water samples and measured the amount of harmful petroleum compounds present in the water. All sampling locations showed non-detectible amounts of petroleum compounds, and one site at Bolsa Chica State Beach had a non-toxic level of certain compounds.
While the results are encouraging, Heal the Bay believes this report alone does not provide enough information to confidently re-open beaches, and we would like more information before we recommend people head out to the beach. Therefore, we continue to have an advisory listed on our Beach Report Card for Orange County beaches. Here are some facts about the report that we would like you to consider before going in the water:
- The report only includes water quality data. Given that petroleum-related fumes pose a health risk to humans (page 2 of report), we would like to see air samples taken as well.
- The data in the report is only from one day of sampling. The City of Huntington Beach has stated that monitoring will take place twice a week, and results will be posted on their oil spill website.
- Only Huntington Beach beaches were sampled. We would like to see data from every beach along the Orange County coast impacted by the spill.
If you do decide to go to the beach, please do the following:
- Avoid contact with visible oil on the sand or in the water.
- Leave the area if you smell oil or gas.
- Report oil sightings to tarballreports@wildlife.ca.gov.
- Shower with soap as soon as you get home.
- Report oiled wildlife sightings to OWCN at 1-877-823-6926.
- Check the Beach Report Card.
WHAT WE KNOW (last updated 10/7)
It began with reports from community members smelling gas on Friday afternoon, and evidence of a visible oil slick on the ocean surface by Saturday. The official announcement of the spill came later Saturday evening: 126,000 gallons of crude oil gushed from a seafloor pipe into the surrounding ocean. The pipeline (owned by Amplify Energy) transports crude oil from the offshore oil platform Elly, located off the coast of Orange County in federal waters, to the shoreline in Long Beach. According to the LA Times, US Coast Guard criminal investigators are now looking more closely into the events leading up to the spill and potential negligence in the delayed response.
Oil spills are terrifyingly toxic to public health and marine life. Beaches are closed, and dead and injured birds and fish are already washing on shore. Marine mammals, plankton, fish eggs, and larvae are impacted too, as this toxic crude oil mixes with the ocean water, spreading both across the water surface and down into deeper water. As of 1:45 PM on October 5, only 4,700 gallons of the 126,000 spilled gallons had been recovered. Sadly this oil has also reached the sensitive and rare coastal wetlands at Talbert Marsh, a critical natural environment not only for wildlife habitat, but also for improving water quality by naturally filtering contaminants from water that flows through; however, this wetland cannot filter out oil pollution on such a scale.

(Photo by City of Huntington Beach)
Major oil spills keep happening because oil companies prioritize profits over the health of people and the environment. This is evidenced by the fact that the oil industry has continuously sought to skirt regulations and loosen up restrictions on oil extraction. The danger posed by the oil industry’s pattern of reckless behavior is augmented when you consider that much of the oil infrastructure in California is decades old and deteriorating. This is the second major pipeline leak in 6 years. The last one in 2015 was the Refugio oil spill that resulted in 142,000 gallons of oil damaging our coastline in Santa Barbara.
Oil spills are part of a much larger pollution problem. The impacts of fossil fuels are felt at every stage, from extraction to disposal.
Major oil spills are disastrous, yet somewhat intermittent. But air pollution from fossil fuel extraction sites and oil refineries located on land have a harmful impact every single day for fenceline neighborhoods. Low-income communities and communities of color are exposed to disproportionate health and safety risks due to a history of abundant drilling within close proximity to where community members live, work, and go about daily life.
So, what does all this risky drilling get us? In the end we are left with products like gasoline, which contributes to the climate crisis when burned, or plastics that are used once (or not at all) and then thrown “away,” ultimately ending up right back here, polluting our neighborhoods and ocean.
WHAT WE DON’T KNOW
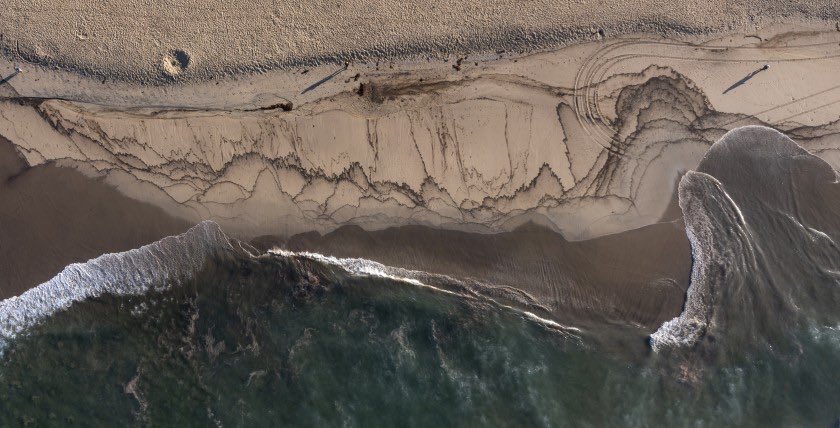
It is still unclear what caused the oil spill as well as exactly when it started and when it stopped. Divers are conducting an ongoing investigation, which will give us more information about what caused the rupture that led to thousands of barrels of oil spilling into the Pacific Ocean.

(Photo by LA Times)
Crude oil is a mixture of toxic chemicals including benzene and other carcinogens, and oil can come in a few different forms, which can have different impacts on the ecosystem. Unfortunately, we do not yet know the type of oil that was spilled, and proprietary trade laws allow oil companies to keep their oil and chemical mixtures a secret. We also do not know how cleanup progress will be monitored and if water quality testing will be included in that process or not. Based on previous spills, we expect the beaches to be closed for several weeks, and we expect environmental harm to last for years.
WHAT NOT TO DO
At this time, the best thing you can do is to stay away from the oil spill area for your own safety.
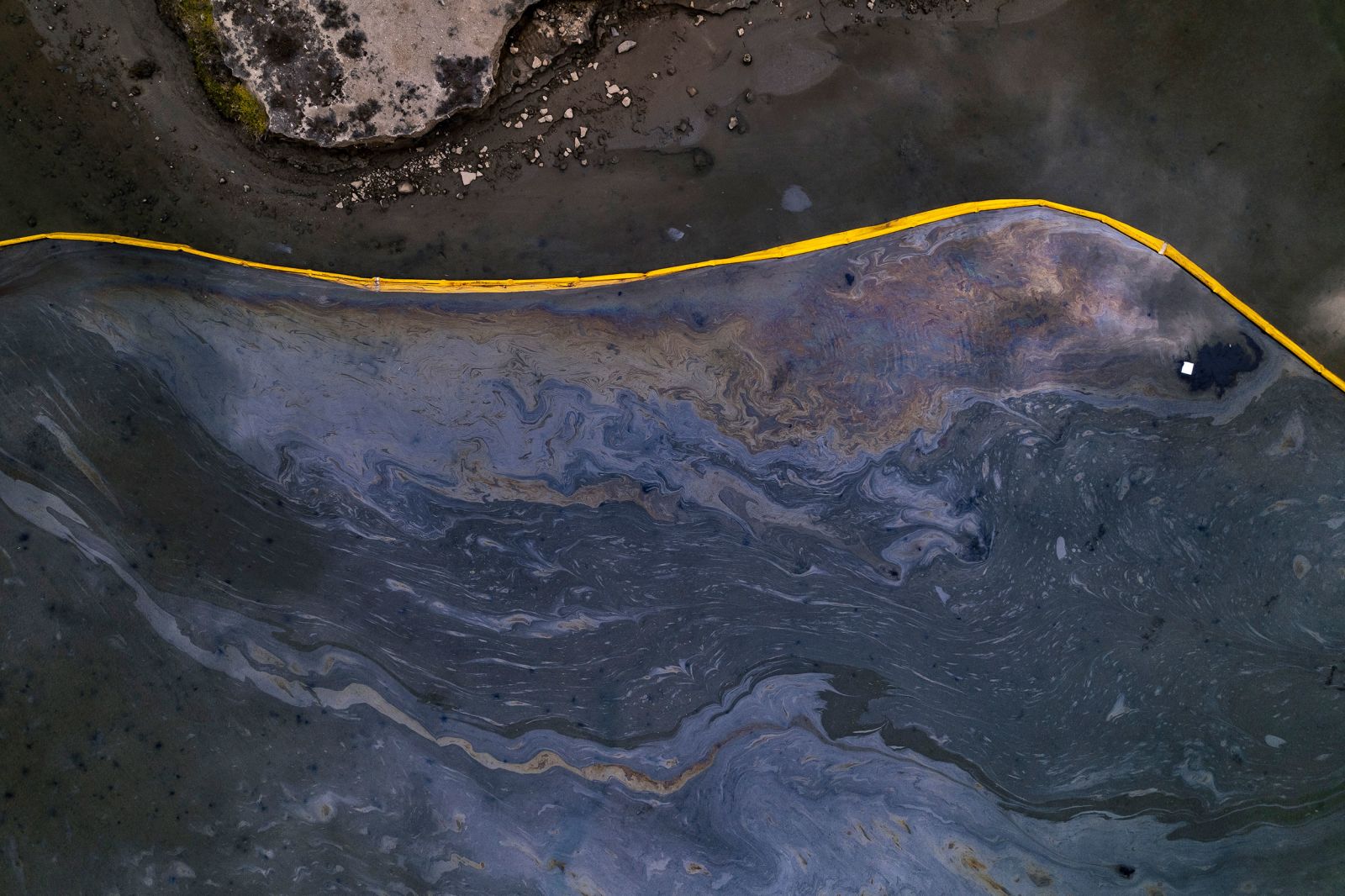
Stay clear of oil-fouled and closed beaches, stay out of the water, and keep boats far from the existing oil slick. As of October 4, Newport Harbor and Dana Point Harbor are closed, and a beach closure has been put into effect in Huntington Beach. Allow plenty of space for rescue workers and cleanup crews from the US Coast Guard and California Department of Fish and Wildlife Office of Spill Prevention and Response (CDFW-OSPR) to access and work at the spill site. If you see any injured or oiled wildlife, DO NOT try to intervene on your own. Instead, report the animal to the Oiled Wildlife Care Network at 1-877-823-6926.
CDFW has issued an emergency fisheries closure between Anaheim Bay and San Onofre Beach. The closure extends 6 to 10 miles offshore. Any take of fish from this area is prohibited until further notice and CDFW is carefully patrolling the area. If you are an angler, check this detailed description and map to ensure you are staying outside the fishing closure for your own health and safety. Shellfish and fish may become contaminated from the oil and other chemicals in the water. Eating fish and shellfish from the contaminated area may make you sick, and it’s also hazardous to be out there fishing because of possible exposure to harmful fumes from the spill.

(Photo by CNN)
WHAT TO DO
Heal the Bay’s Science and Policy team is working on a public call to action with specific policy demands that we will share soon on our blog and on our Twitter, Instagram, and Facebook channels. In the meantime, there is still a lot that you can do while keeping a safe distance from the oil spill.
If you are local, you can volunteer with spill cleanup efforts. The California Department of Fish and Wildlife is soliciting volunteers from the public to assist in volunteer tasks with the Unified Command.
You can contact the UC Davis Oiled Wildlife Care Network at 1-877-823-6926 to report oiled wildlife. Currently, only trained responders may assist in the cleanup efforts. However, if you would like to sign up to be trained for future emergencies, you can fill out this OSPR Incident Volunteer Form, or call the volunteer hotline at 1-800-228-4544 for more information.
You may encounter tarballs on San Diego and Orange County beaches. Oil contains hazardous chemicals, and for safety reasons we recommend not handling tarballs or any oil yourself. If you encounter tarballs, contact cleanup teams at tarballreports@wildlife.ca.gov for assistance.
Stay informed! Review the news and reports, follow the Southern California Spill Response for information and updates, and keep tabs on the Los Angeles Times, which is doing in-depth and up to date reporting during this emergency.
We encourage you to support and follow these organizations doing great work to rescue and protect wildlife from the oil spill and champion clean water and healthy wetlands locally in Orange County:
Oiled Wildlife Care Network
Pacific Marine Mammal Center
International Bird Rescue
Wetlands and Wildlife Care Center
OC Coastkeeper
Bolsa Chica Conservancy
Huntington Beach Wetlands Conservancy
Newport Bay Conservancy
We suggest you follow and support these organizations who are tirelessly taking on the big fight to phase out oil drilling in our ocean, neighborhoods, and everywhere else:
Sacred Places Institute for Indigenous Peoples
Communities for a Better Environment
Azul
STAND-LA coalition
Last Chance Alliance coalition
Center for Biological Diversity
Sierra Club
Surfrider
East Yard Communities for Environmental Justice
Heal the Bay (that’s us!)
This is NOT an exhaustive list; there are many organizations and individuals doing this hard work. If your group is working on the spill or fighting big oil and would like to be added to the above list, contact us.
THE TAKEAWAY
If we continue to rely on fossil fuels, oil spills and air pollution are inevitable and their impacts will continue to be devastating. The only solution is to shut down this dirty industry and protect ourselves and our environment through a just transition away from an extractive fossil fuel economy.
Here’s how to take action.
This post was originally published on October 5, 2021 and will be updated as new information is provided.