Photo credit: Ashlee Malyar, Marine Mammal Volunteer
Heal the Bay MPA Watch intern, Alex Preso, saw a distressed seal pup while conducting beach surveys, and helped it get the care it needed by alerting the California Wildlife Center. Alex shares what happened, plus the “Do’s” and Don’t’s” of helping a marine mammal in distress.
At first I thought it was a piece of driftwood on the beach… it was actually a distressed seal pup.
On Wednesday, March 18, I was taking surveys for Heal the Bay’s MPA Watch Program on El Pescador Beach in Malibu. As I was making my way along the beach, I noticed what looked like a washed-up log in the distance. As I moved closer, I realized that it was actually a small seal. The seal was lying on its back, barely moving, and was thin with wrinkled skin. It looked noticeably uncomfortable and I immediately suspected that something was wrong.
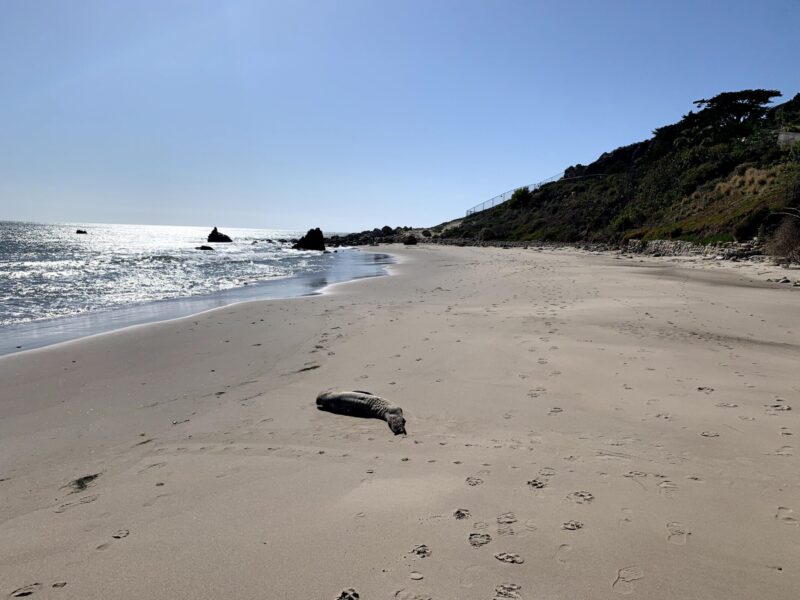

Sometimes a seal pup like this one simply struggles to survive on its own after separating from its mother, but there are also a variety of human impacts that can cause a marine mammal to be in distress.
1) First, plastic debris in the ocean or on beaches poses a significant threat to marine mammals. When ingested, these animals cannot digest the plastic, so it stays in their bodies. This plastic can leach harmful chemicals into their bodies or even block their digestive tract, leading to starvation and malnourishment. Heal the Bay is working to combat this through our plastic pollution and beach cleanup programs. These programs aim not only to help remove plastic from our oceans, but also to keep this harmful marine debris from entering our oceans in the first place.
2) Second, overfishing of important food sources for marine mammals limits available nourishment and puts these animals at risk. Heal the Bay’s sustainable fisheries work aims to maintain healthy fisheries so that these animals have abundant food sources.
3) Third, loss of habitat can endanger marine mammals. Heal the Bay’s MPA program helps to monitor protected areas that are critically important to protecting these habitats, so that these animals have safe places to live, reproduce, and find food.
4) Fourth and finally, poor water quality can cause marine mammals to become sick. Polluted water can cause a variety of health issues for marine mammals, including bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections. Heal the Bay’s water quality work aims to prevent harmful bacteria, toxins, and other pollutants from ending up in the ocean and endangering marine life.
Heal the Bay is doing what we can to prevent these threats to marine mammals, but while these issues persist, it is important that we all keep an eye out for stranded marine mammals on our local beaches.
But even if you see a seal on the beach, how can you tell if it is in danger or simply catching some rays?
Many people don’t know how to tell if an animal like this is actually in trouble, let alone what actions to take if it is distressed. When I encountered this young seal, I saw many other people walking along the beach, barely taking notice of the animal.
Here is are some clear signs that a marine mammal is in distress and in need of help:
- visible entanglement in trash or fishing gear
- visible malnourishment or open wounds
- a young pup without an adult nearby
- erratic behavior
Fortunately, you don’t need to be an expert to help a seal in need. If you suspect that a marine mammal may be in distress, always call the appropriate rescue hotline. It is better to have the rescue crew come to the beach to find a healthy animal than to leave an animal in distress without help. The numbers to call vary by location and are listed below.
Here are a few things to avoid if you find a distressed marine mammal:
- DO NOT touch or approach the animal
- DO NOT attempt to return the animal to the water
- DO NOT pour water on the animal
- DO NOT attempt to move the animal
If you wouldn’t want someone to do it to you while you’re sunbathing on the beach, chances are the animal wouldn’t like it either. Marine mammals intentionally seek out dry land when they are in distress so that they can rest and soak up the sun.
What you should do if you find a distressed marine mammal:
- DO stay approximately 50 feet away
- DO call the appropriate rescue hotline
- DO take a picture of the animal
- DO try to pinpoint the animal’s location
- DO wait near the animal until the rescue crew arrives

The number for the rescue hotline varies by location, but any of them can connect you to the correct region if you do not have the right number.
- For animals found in San Pedro up to Pacific Palisades (including all beaches between them) – call Marine Animal Rescue # 1-800-399–4253 [WHALE]
- For animals found in Malibu – call the California Wildlife Center # 310-458–9453 [WILD]
- For animals found in Long Beach – call Long Beach Animal Control # 562-570–7387
When you call the hotline, they will ask you to send a photo of the animal as well as its location. Try to be as precise as possible so that they can save time and arrive at the animal directly.
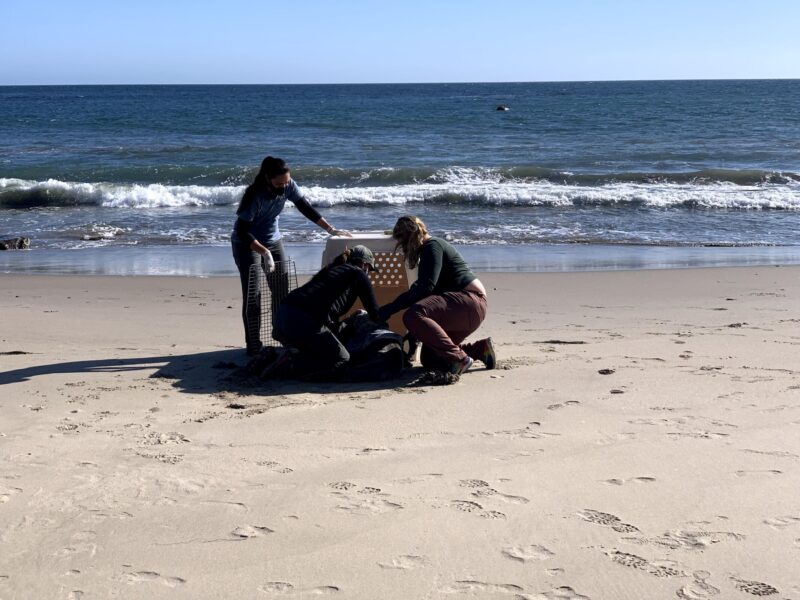
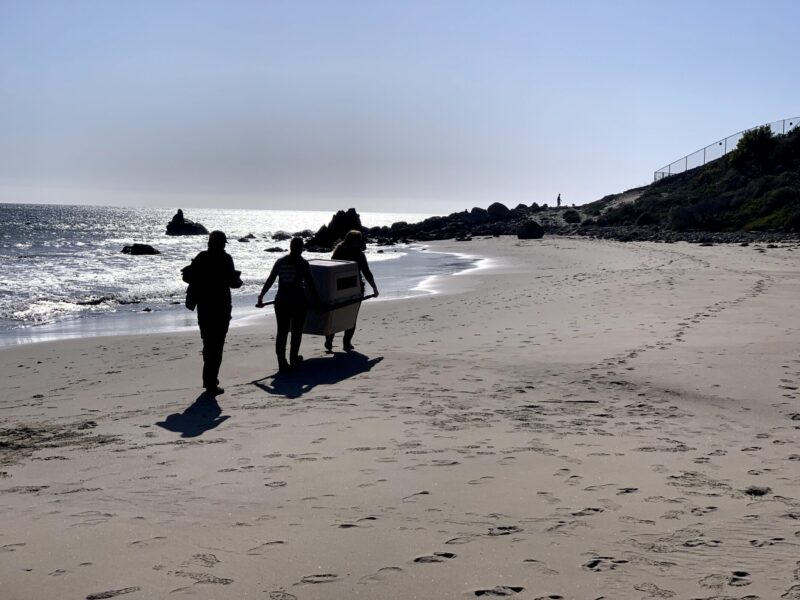
In this instance, I called the Malibu number. Then I waited with the seal for about 30 minutes until the rescue crew arrived at the beach. While waiting, I was careful to keep my distance from the seal and ensured that other passersby did so as well. When the crew arrived, they expertly loaded the seal into a crate and took him back to their facility for rehabilitation.
Later, I learned that this animal was a 12 week old elephant seal pup that was badly malnourished. He had shrunk back down to his birth weight of about 75 pounds when he should have been closer to 300 pounds. They named him “Yellow” because they used a yellow marker to make an identifying mark on him while in their care.
The California Wildlife Center (CWC) is permitted by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) to provide rehabilitative care to seals and sea lions. They will rehabilitate Yellow and help him gain the necessary body weight and skills to better fend for himself before returning him to the wild. All of the animals they rescue stay in their facility temporarily, as their mission is to rehabilitate and return marine mammals to the wild where they belong.
For Yellow, the outlook is bright and he is expected to be released back into the wild in May. This instance just goes to show that a chance encounter on the beach can be the difference between life and death for a marine mammal. It was for Yellow.
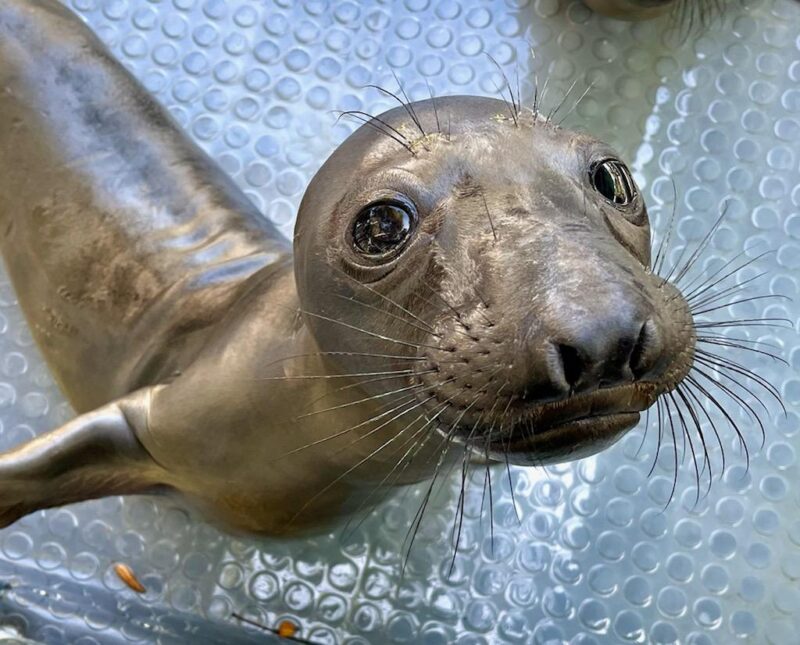

Photo credit: Ashlee Malyar, Marine Mammal Volunteer
Support our work: