Glow Up: Bioluminescence & Biofluorescence in the Bay
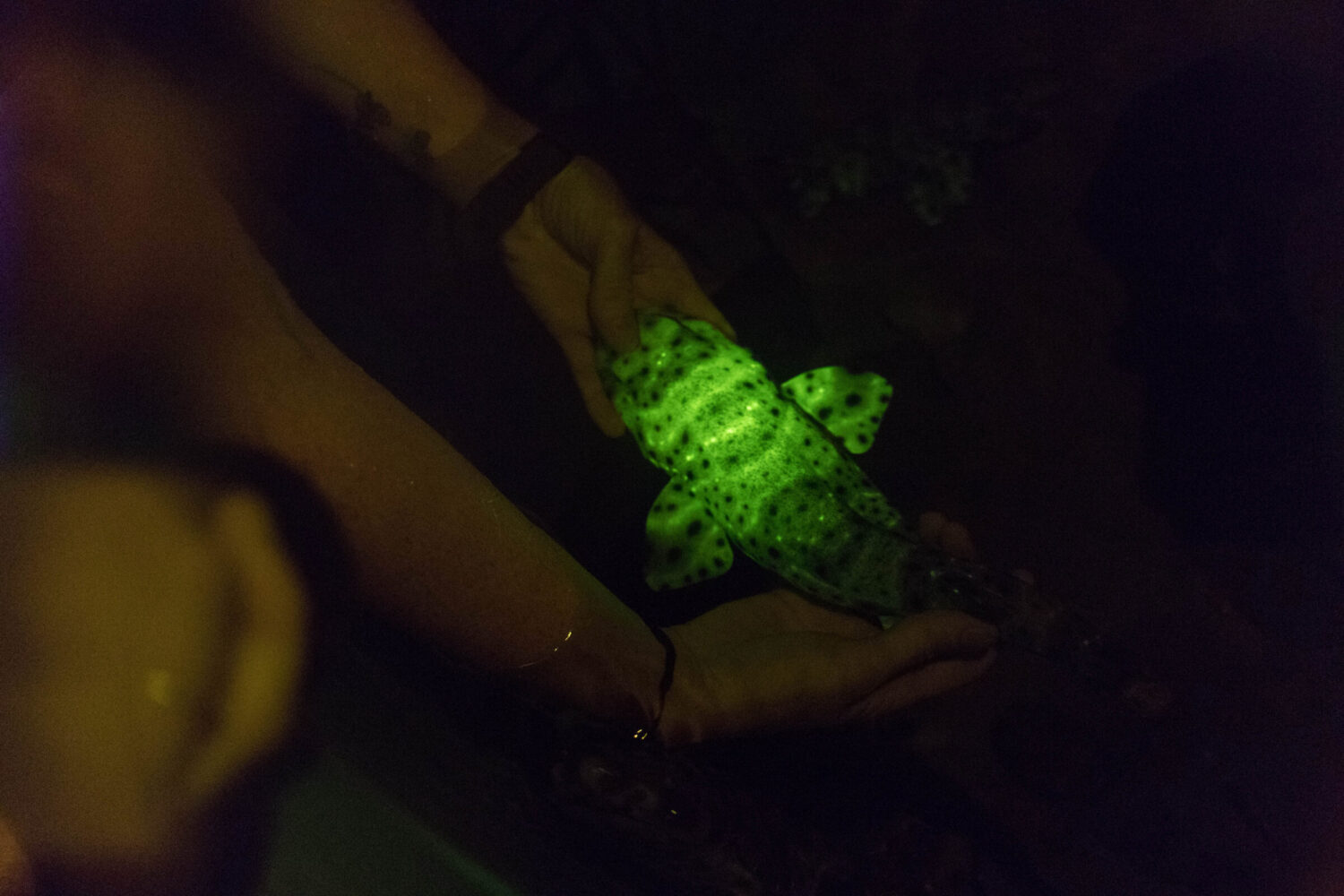

Laura Rink, Heal the Bay Aquarium’s Associate Director of Operations, deepens our understanding of biofluorescence in the Santa Monica Bay and shares how local ocean animals get their glow on.
When you think about a rainbow, what comes to mind?
A beautiful archway of color after a rain? A favorite multi-colored candy? A representation of equality for all? Or perhaps the engrained acronym from early childhood, ROY G BIV (Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, and Violet)?
Regardless of what comes to mind, one thing holds true: the colors of the rainbow are what make up visible light. This fact, however, does not hold true as one enters the world beneath the waves of the ocean. In many instances, ocean animals have the unique capability to see what humans consider to be invisible light, illuminating their world in a unique and fascinating way.
Light greatly governs our lives (think sunrises, sunsets, light bulbs, traffic lights, and rocking out to the song “Blinded by the Light”). Light also plays a large role in the life of ocean animals.
Frequently, ocean animals use light as a form of adaptation for recognition, protection, or attraction. A commonly known use of light in the ocean is called bioluminescence. Examples of bioluminescence include firefly butts, glowing algae, and that oogey boogey fish of the deep that uses a light lure dangling from the top of its head to attract unsuspecting prey. This type of glow adaptation is a chemical process animals use to create light. See the most recent example of bioluminescence in the Santa Monica Bay in April 2020.
More recently scientists have discovered a variety of ocean animals with a protein in their skin that reflects ultraviolet light through a process called biofluorescence. How this works is the protein in the animal’s skin absorbs low energy ultraviolet blue light from the sun and reflects it at a higher energy, resulting in either a green or red fluorescent glow. This is similar to how the ink of a highlighter glows as you streak it across a textbook page, emphasizing a sentence you need to remember for a pop quiz later.
What animals might use this illuminating process, you wonder?
If we dive into the Santa Monica Bay and other Pacific Ocean areas in Southern California we find swell sharks, spiny lobsters, Kellett’s whelk snails, and a large variety of anemones who all get their glow on.
Although the specific reason that each species glows is not entirely certain, scientists hypothesize that some ocean animals, such as swell sharks, use this process to help identify individuals. Sort of like the identifying spots on a cheetah or a unique birthmark on a human, only much brighter.
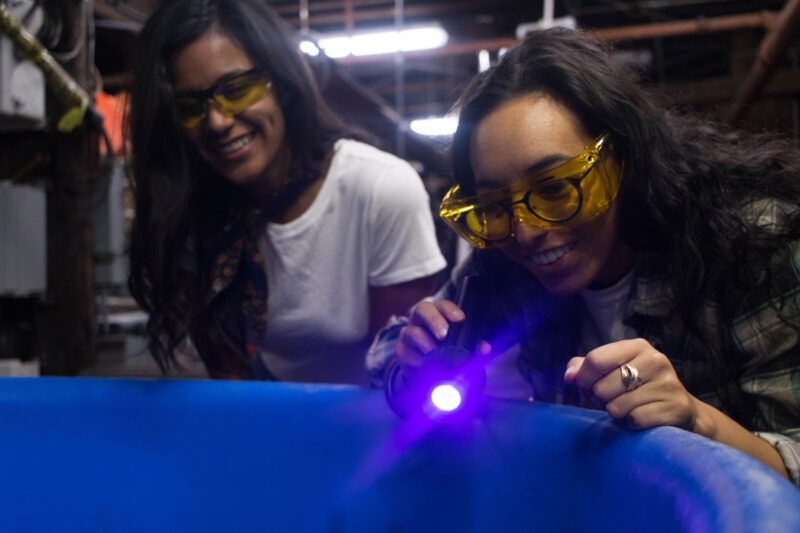

Why has it taken scientists so long to discover the biofluorescent glow of ocean animals? Most human eyes are only capable of seeing the colors of light from the rainbow and cannot see the glow of bioluminescence without some extra help. Through the use of a strong ultraviolet light source and blue light blocking lenses, humans are able to see the glow that certain types of ocean animals naturally see with their uniquely adapted eyesight.
If you would like an opportunity to see ocean animals glow and learn more about this dazzling process, stay tuned for our Heal the Bay Aquarium special night event series: “Go With the Glow”*. Guests can take a tour of our Aquarium’s darkened gallery to see the spectacle of biofluorescence in the ocean.
*Our Go With the Glow event series is postponed to accommodate physical distancing and help prevent the spread of COVID-19. Please sign up for our next event dates on July 3 and September 4.