July 14, 2016 — This past spring Heal the Bay hosted our first-ever BioBlitzes at two of Los Angeles’ remaining wetlands: Malibu Lagoon and Ballona Wetlands. BioBlitzes bring people together to rapidly (over a period of a few hours) catalogue and identify plant and animal life in biodiverse areas. Wetlands are unique and critical ecosystems that are in trouble – in the last couple hundred years, Southern California has lost over 90% of its native wetlands.
Wetlands provide many services, which often go by unappreciated. They help regulate climate, store surface water, control pollution and flooding, replenish natural aquifers, protect shorelines, maintain natural communities of plants and animals, and provide opportunities for education and recreation. (For more information about Southern California’s wetlands, check out http://scwrp.org/general-wetlands-information/). Unfortunately, years of development and degradation have destroyed the flow of water, altering the habitat for wetland animals and plants. Heal the Bay supported the restoration of Malibu Lagoon from 2012 to 2013 and now we’re lobbying for the restoration of Ballona Wetlands as well to bring it back to a healthy, functional state. Our BioBlitz events helped capture and illuminate the amazing biodiversity of these areas. After crunching the numbers from these events, it seems timely to share our findings leading up to this Saturday’s beach cleanup and sneak peek at the Ballona reserve.
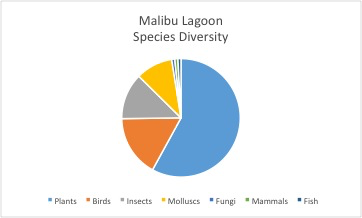 Most of our observations were of the amazing plants that rely on the wetlands to thrive. Plants form this environment’s base, providing a natural filter for water as it passes through. They also provide habitat, food, and shelter for the populations of birds, insects, and reptiles that live in wetlands. We found both sites were host to dozens of bird species including great blue herons, snowy egrets, and brown pelicans. Every year, almost one billion birds migrate along the coast of California in an area known as the Pacific coast flyway. Wetlands in Southern California are a crucial pit stop for migratory birds and the diversity of species we observed is promising. In just three hours at Ballona, we saw 17 different species of birds – almost a third of the bird species found in an extensive wetlands survey conducted by The Bay Foundation that spanned months. This shows the power of BioBlitzes to capture important data for conservation.
Most of our observations were of the amazing plants that rely on the wetlands to thrive. Plants form this environment’s base, providing a natural filter for water as it passes through. They also provide habitat, food, and shelter for the populations of birds, insects, and reptiles that live in wetlands. We found both sites were host to dozens of bird species including great blue herons, snowy egrets, and brown pelicans. Every year, almost one billion birds migrate along the coast of California in an area known as the Pacific coast flyway. Wetlands in Southern California are a crucial pit stop for migratory birds and the diversity of species we observed is promising. In just three hours at Ballona, we saw 17 different species of birds – almost a third of the bird species found in an extensive wetlands survey conducted by The Bay Foundation that spanned months. This shows the power of BioBlitzes to capture important data for conservation.
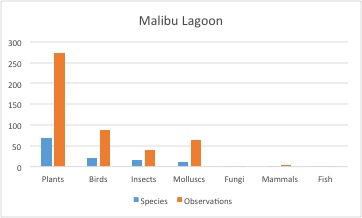 From 2012 to 2013, Heal the Bay advocated for an ecological restoration of Malibu Lagoon which involved removing invasive species, replanting native ones, and adjusting the hydrology of the wetland. Inventories done by The Bay Foundation showed only six species of native plants prior to restoration, while almost 41 were noted after the restoration! Since plants form the base of an intricate web of life in the wetlands, bringing back natives can also bring back other species – including those that are threatened. At both sites our BioBlitzers found four threatened species, but that number will certainly increase with more sampling.
From 2012 to 2013, Heal the Bay advocated for an ecological restoration of Malibu Lagoon which involved removing invasive species, replanting native ones, and adjusting the hydrology of the wetland. Inventories done by The Bay Foundation showed only six species of native plants prior to restoration, while almost 41 were noted after the restoration! Since plants form the base of an intricate web of life in the wetlands, bringing back natives can also bring back other species – including those that are threatened. At both sites our BioBlitzers found four threatened species, but that number will certainly increase with more sampling.
We found more than 20 introduced species at each site, which means they arrived through human influence. These invaders include everything from the delicate cabbage white butterfly to the crystalline ice plant. Invasive species are one of the biggest threats to healthy wetlands because they can outcompete native species and overtake the habitat. Since the restoration at Malibu Lagoon, the pervasiveness of non-natives has decreased. While Ballona is still struggling with invasive species, we hope planned restoration efforts will allow this wetland to reach its full potential.
Thanks to all of our “blitzers” for helping us Blitz the Bay in Ballona Wetlands and Malibu Lagoon. Keep exploring, enjoying, and fighting for our wetlands!
Citizen Science Coordinator Catherine Hoffman led these successful blitzing efforts.
 |
 |


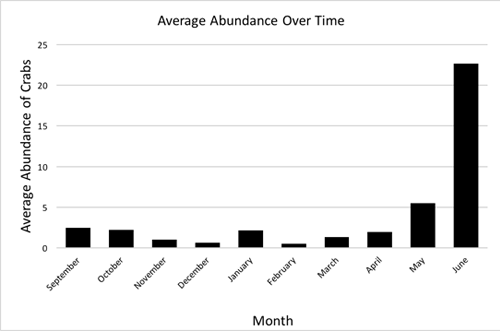
 Taylor Spesak is the Aquarium’s public programs educator. Join him every Wednesday at 3pm for sand crab monitoring. The program is included with
Taylor Spesak is the Aquarium’s public programs educator. Join him every Wednesday at 3pm for sand crab monitoring. The program is included with  It was especially gratifying to see Mark Gold, past Heal the Bay president and current board member, in attendance. Amid often fierce opposition from city officials and some Malibu property owners, Gold led the charge to demand an end to septic tanks in the Civic Center area for many years. He helped broker an MOU between the city and the regional water board that phased out septic tanks and mandated the building of a more modern treatment facility. (You can read more about his war wounds in one of his blog posts
It was especially gratifying to see Mark Gold, past Heal the Bay president and current board member, in attendance. Amid often fierce opposition from city officials and some Malibu property owners, Gold led the charge to demand an end to septic tanks in the Civic Center area for many years. He helped broker an MOU between the city and the regional water board that phased out septic tanks and mandated the building of a more modern treatment facility. (You can read more about his war wounds in one of his blog posts  Julie Potyraj is the community manager for
Julie Potyraj is the community manager for 


