The Future of California MPAs: Insights from the Experts
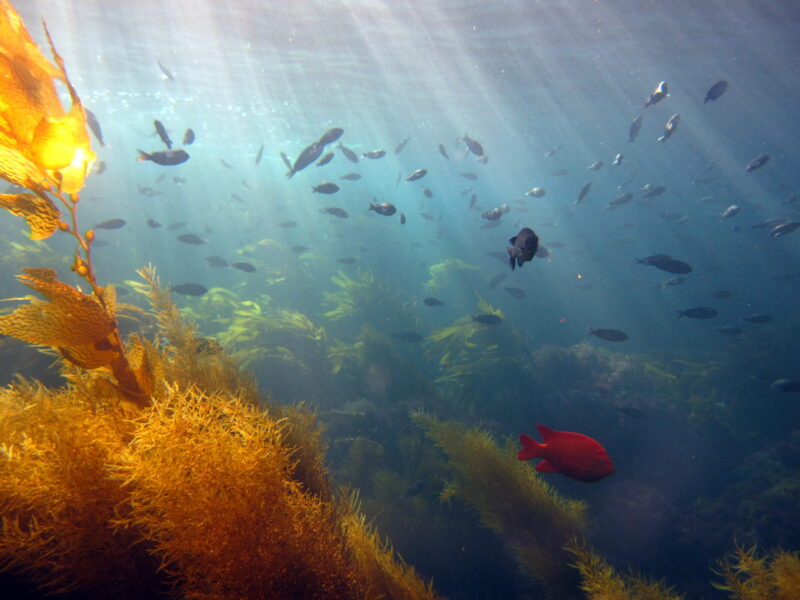

Like a national or state park on land, Marine Protected Areas, or MPAs, conserve and protect wildlife and habitats in the ocean. Here in California, we have a unique and science-based network of 124 MPAs all up and down the coastline. This network exemplifies a new kind of MPA science, designed to not only conserve the habitat inside the boundaries of the protected areas, but to enhance the areas in between as well.
The MPA Decadal Review
California’s MPA network has been around since 2012 and, per the Marine Life Protection Act (MLPA) passed in 1999, this network must be reviewed every 10 years. This year marks the very first Decadal Management Review of California’s MPAs. What does that mean for our network?

To get started, California’s MPAs are really special – what makes our network of 124 MPAs different from other MPAs in the United States and around the world?
Most MPAs around the world are designed as individual protected areas: a specific spot on the map that is set aside and conserved. Our MPAs are different; they span the entire California coastline and are ecologically designed as a network. They are meant to interact with each other, connected by the California Current, wildlife migration, and dispersal patterns.
Since California’s MPAs are a statewide network, we can actually manage them as a state. All 124 MPAs are managed to the same degree, unlike MPAs that are managed differently region by region. This allows for more equitable distribution of resources, no matter how remote an MPA may be.
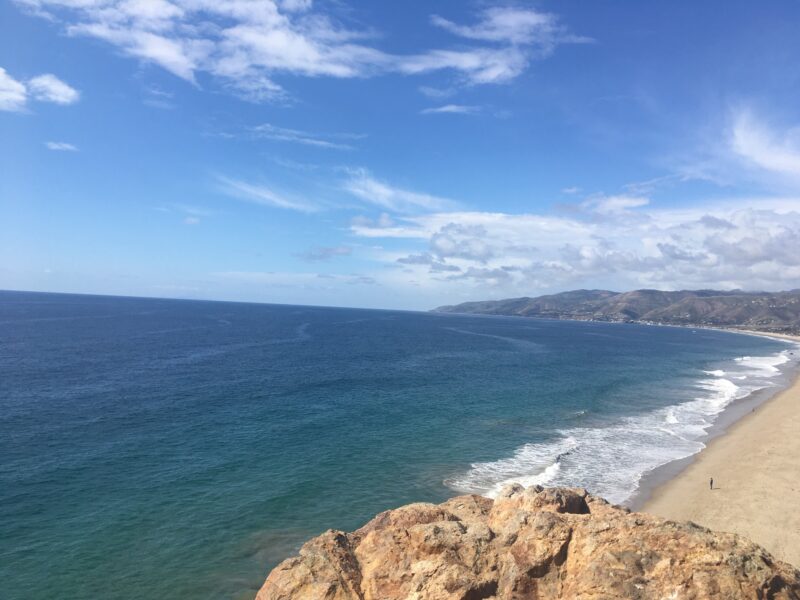

Point Dume is one of 124 stunning Marine Protected Areas in the state that offer safe refuge for ocean inhabitants as well as breath taking views from the land that make up the California Coastline.
The state of California manages our entire MPA system, how exactly does that work?
We use “adaptive management” for our network of MPAs in California, which gives us an opportunity to change how we manage these areas as the ecosystems change over years or decades. What might be working in MPA management now, might not work in the future. It was quite brilliant to include adaptive management in the MLPA and we are already seeing now, with the climate changing so rapidly, how necessary it was.
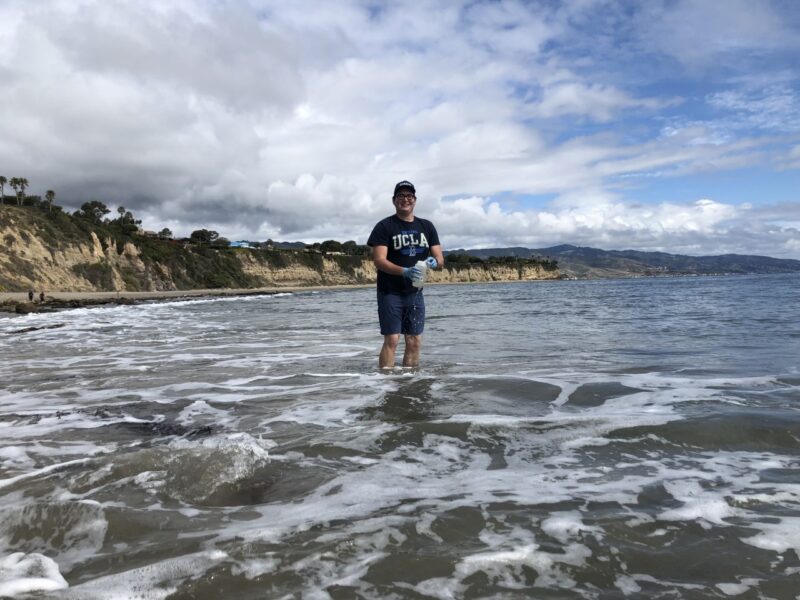

A variety of information is taken into account when monitoring an MPA. Heal the Bay partnered with scientists like PhD candidate Dr. Zack Gold to study eDNA in protected waters over the past couple years.
A key part of adaptive management is checking in on our MPAs to see how they are working and then adapt management accordingly. Here in California we do that through the Decadal Management Reviews, and the very first one is happening this year. Tell us about this review.
The Decadal Management Review, which was written into the MLPA, is an opportunity for us to use science and monitoring to see what has been going on in MPAs over the past 10 years. Based on the evidence presented, we can determine if there are any ways we can strengthen MPA management to make it more effective.
What does this scientific evidence look like?
The state of California has been funding long term MPA monitoring for a long time, and it all started with baseline data. Researchers went to all different types of ecosystems like sandy beaches, rocky reefs, kelp forests, and estuaries and gathered information to get an idea of what was going on inside and outside MPA boundaries 10 years ago, before the MPAs were put into place. Since then, those same sites have continued to be monitored over time to look at changes and see if anything interesting has happened since the baseline data was collected. In addition to the long-term data sets, we also will be interested in community science, like MPA Watch, to give a broader picture of the human dimension of MPAs [how humans interact with, use, impact, and value these areas]. The review will also include Traditional Ecological Knowledge from Indigenous communities who have been stewards of these lands and waters since time immemorial.

MPA volunteers like Sophia von der Ohe (seen in the picture above) are crucial to the success of the Decadal Review. Over 36161 surveys have been submitted by MPA watch volunteers to date.
How exactly will the review work, and who is involved?
The major players are the California Fish and Game Commission (FGC), the California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW), and the California Ocean Protection Council (OPC). The review will start with the gathering and synthesizing of scientific evidence by CDFW – this is happening right now and will continue through the year [and Heal the Bay is helping to contribute evidence and data for this critical step]. As the managing agency of the MPA network, CDFW will present this evidence to the FGC through a report, a presentation at a Commission meeting, and a symposium. This is set to happen in early 2023. As the regulatory body, the FGC will then review the evidence and make the decision if any changes are needed in MPA Management. If they choose to make any changes, they would have to go through a full regulatory process.

What can we expect from this first review? Will the science show major changes? Will there be any big management adjustments like MPAs added/removed or shifting boundaries?
The science might show some changes [like this Channle Islands MPA study showed increased abundance and biodiversity] but we don’t know yet because we are still analyzing that data. These are cold water climates and here, things take a long time to change. So, even though we are reviewing the science every 10 years, and we will see some interesting things, this review isn’t going to definitively show an extremely different landscape from 10 years prior.
We don’t expect any major management adjustments during this first 10-year review, such as border changes, adding new MPAs, or removing current MPAs. If you have heard that this management review is going to determine whether or not we are going to keep our MPA network or not, that is not this case: this review isn’t like a pass-fail test.
What you CAN expect from this review is a very interesting narrative and look back on the past 10 years of MPA management. We will see the amount of effort that was needed to manage our MPAs and interesting ecological data and stories. We will see data on the human dimension, such as community science, socioeconomics, how communities have interacted with their MPAs, and a review of the resources that were put into the network. This review will help to show the international global significance of this network and how other managers are looking to us as an example.
How can folks get involved in the review process?
The state is working to involve all ocean users and MPA stakeholders in the review process. If you are interested in getting involved in the review, you can:
1. Submit comments to CDFW for the review on their webpage
2. Stay informed by signing up for CDFW’s mailing list or learning more on their FAQ page
3. Attend FGC meetings and give a public comment
4. Get involved in the science! Join Heal the Bay’s MPA Watch program or The California Collaborative Fisheries Research Program to help collect important data used for the review
5. Go visit your MPA! We have four gorgeous MPAs here in LA County where you can swim, hang on the beach, surf, whale watch, snorkel, or tidepool!
So, folks, there you have it! All the information you need on California’s 2022 MPA Decadal Management Review. To close, some words of advice from an MPA: Be adaptive, base your decisions in science, protect yourself, get by with a little kelp from your friends, and do your own decadal review!