Marketing/Communications Intern Darrin Moret got a behind-the-scenes peek at the Santa Monica Pier Aquarium’s newest exhibit. An LMU class of ’13 alumnus, Darrin is a writer and enjoys the beach, surfing and travel.
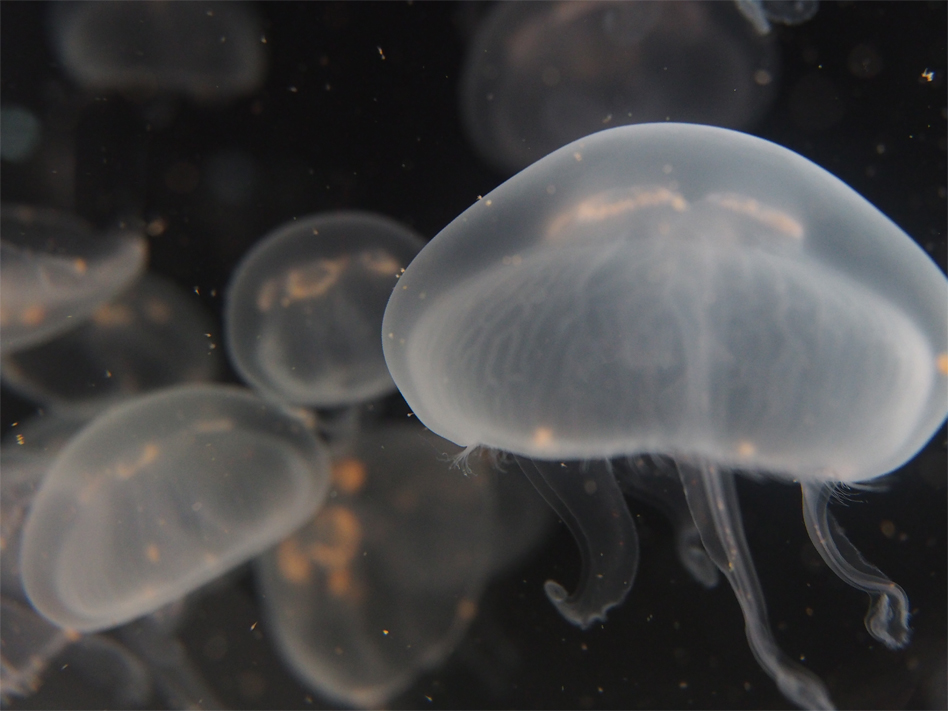

There’s more to see than what meets the eye at the Santa Monica Pier Aquarium these days. It’s the little guys that are the stars of the show at “Catch of the Day”—a refreshing new exhibit utilizing cutting-edge digital imaging technology to shine the spotlight on some of the Bay’s smallest critters. Tanks filled with sea stars, snails, hermit crabs and California killifish now await visitors along with the Aquarium’s more established eel, ray and shark residents.
This dynamic exhibit highlights species of local marine life often overlooked in traditional aquarium displays, using a high-definition digital microscope camera and monitor to allow patrons to view these creatures at a level of detail not possible with the naked eye. “You really get a close look at little things most people miss,” says José Bacallao, the exhibit’s designer and the Aquarium’s Senior Aquarist and Operations Manager.
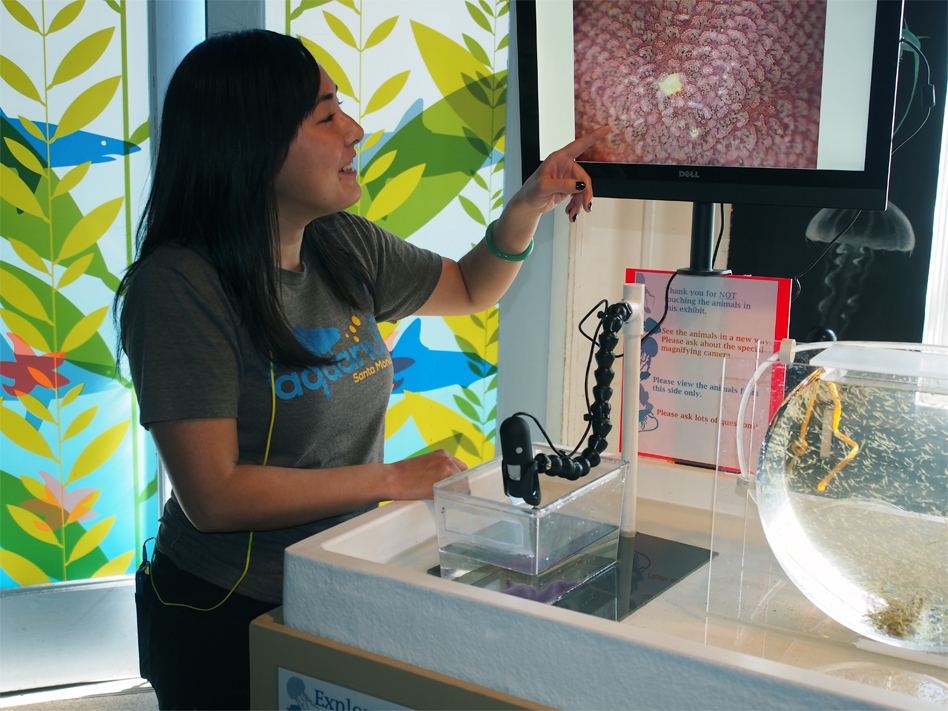

While small, many of the species featured in the exhibit form an integral part of the food web in the local marine ecosystem. Some of the fish that may be found in the tanks, including juvenile black surfperch, are important gamefish that support a thriving recreational fishery and are commonly caught by anglers off the Santa Monica Pier.
Nestled under the Pier’s wooden deck and beneath the historic carousel, the Santa Monica Pier Aquarium could easily be missed by anyone visiting the more conspicuous attractions topside. However, for those who make it inside, this aquarium provides a unique opportunity to learn more about the marine ecosystem that thrives just offshore. Patrons young and old take delight in getting an up-close look at horn sharks in an open-top tank, initiating staring contests with moray eels and touching (gently, of course) a variety of invertebrate species in the touch tank. In an effort to keep their exhibits fresh and exciting for visitors, José and his team periodically update the tanks with newly collected specimens for viewing.
 While it may be the fish that draw most of the attention, it is the Santa Monica Pier Aquarium’s dedicated team of aquarists and volunteers that really make this place special. In addition to maintaining exhibits and informing visitors about marine life, they share a passion for helping protect the ocean by stressing the importance of environmental stewardship. José says his love for working with animals and his staff at the Aquarium is the most exciting thing about his job, his enthusiasm for which is apparent to anyone in his presence.
While it may be the fish that draw most of the attention, it is the Santa Monica Pier Aquarium’s dedicated team of aquarists and volunteers that really make this place special. In addition to maintaining exhibits and informing visitors about marine life, they share a passion for helping protect the ocean by stressing the importance of environmental stewardship. José says his love for working with animals and his staff at the Aquarium is the most exciting thing about his job, his enthusiasm for which is apparent to anyone in his presence.
For a closer look at the “Catch of the Day” and other exhibits, drop by the Santa Monica Pier Aquarium Tuesdays through Fridays from 2:00 to 5:00 p.m., and weekends from 12:30 to 5:00 p.m. Admission is free for kids 12 and under and $5 for visitors 13 and older. In 2015, the first Wednesday of every month is free, thanks to the generous sponsorship of Wells Fargo.
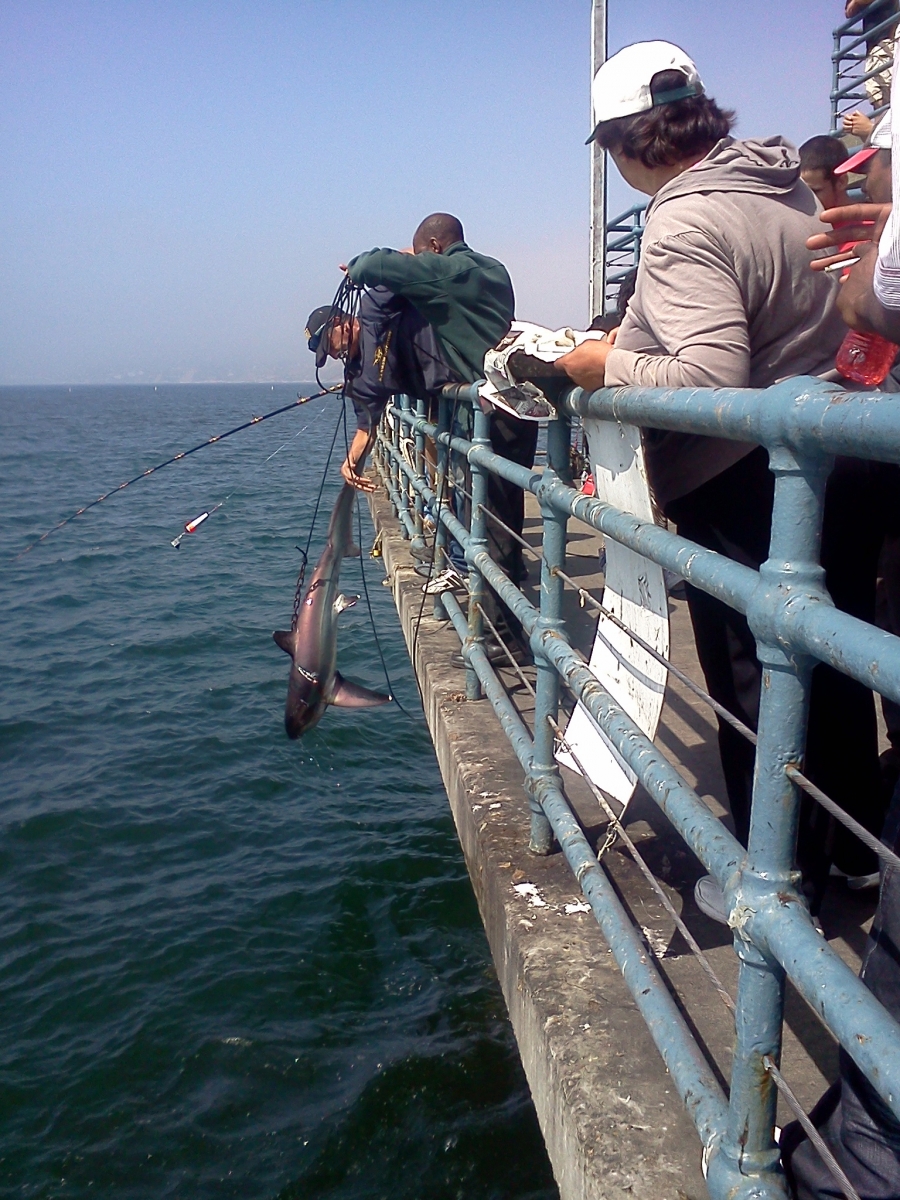
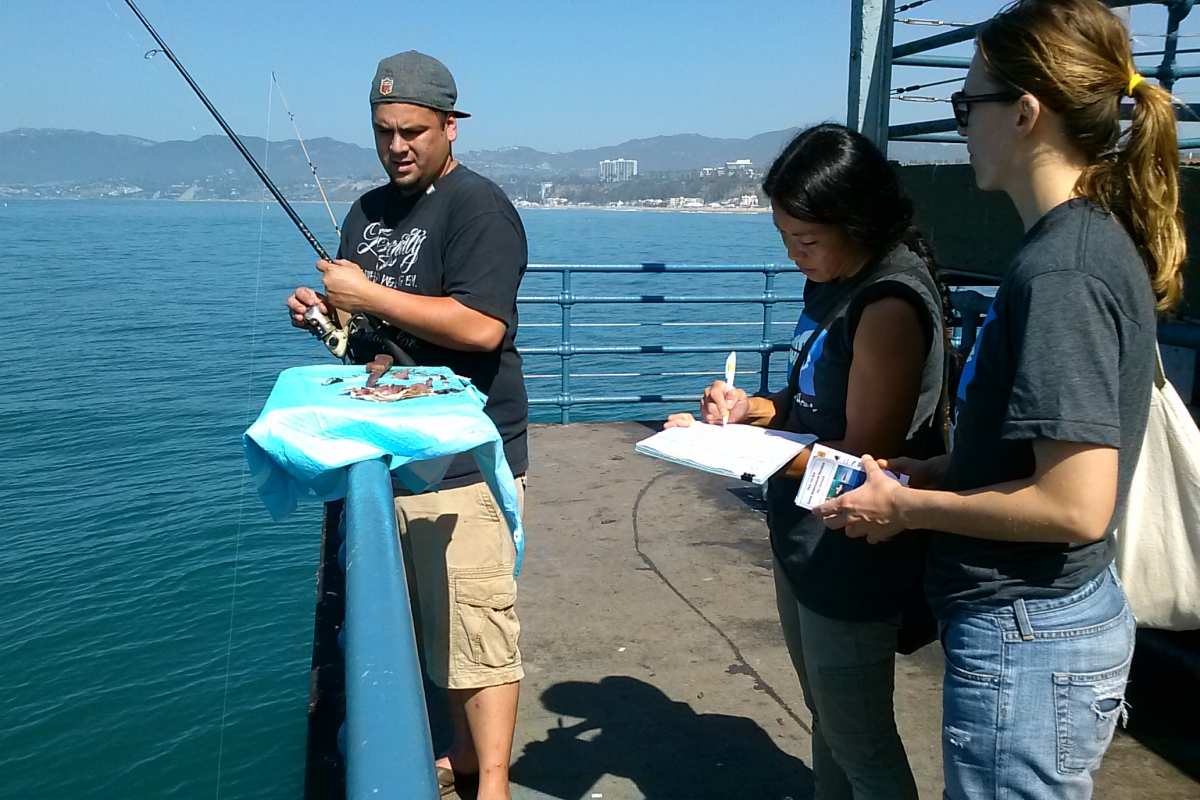


 Our Shark Ambassadors talk with an angler at the S.M. Pier.
Our Shark Ambassadors talk with an angler at the S.M. Pier. 

 Hartley, right, exploring PV Peninsula with our senior aquarist Jose Bacallao
Hartley, right, exploring PV Peninsula with our senior aquarist Jose Bacallao Spiny lobsters are most active night, posing some challenges for divers.
Spiny lobsters are most active night, posing some challenges for divers.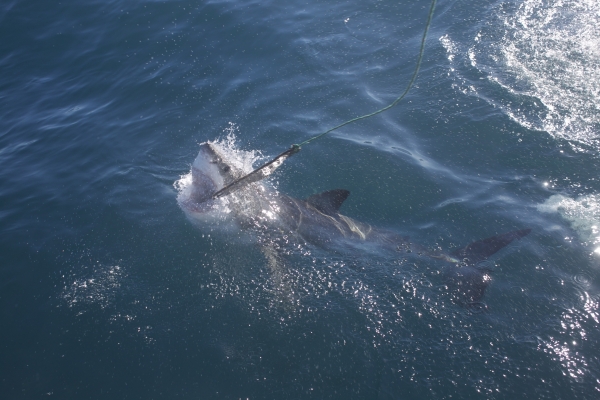 A white shark takes the bait in Shark Alley off the coast of South Africa.
A white shark takes the bait in Shark Alley off the coast of South Africa.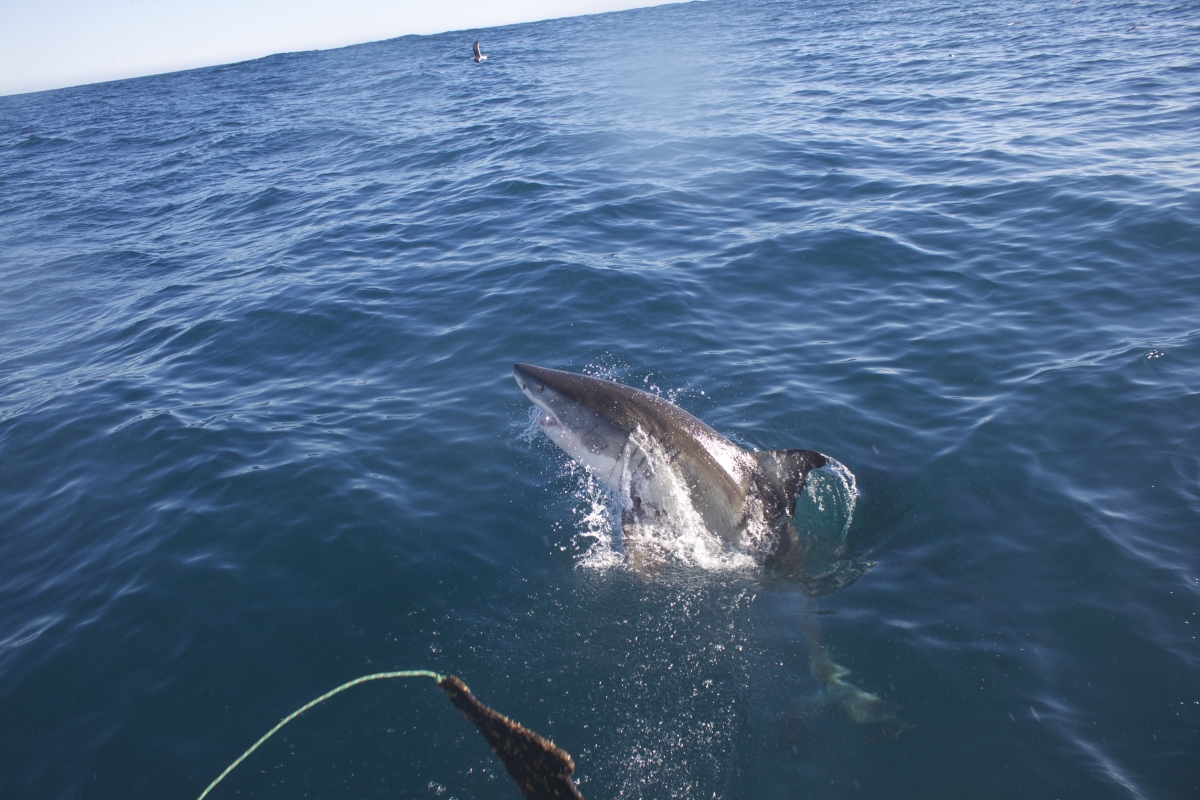 A white shark breaching.
A white shark breaching.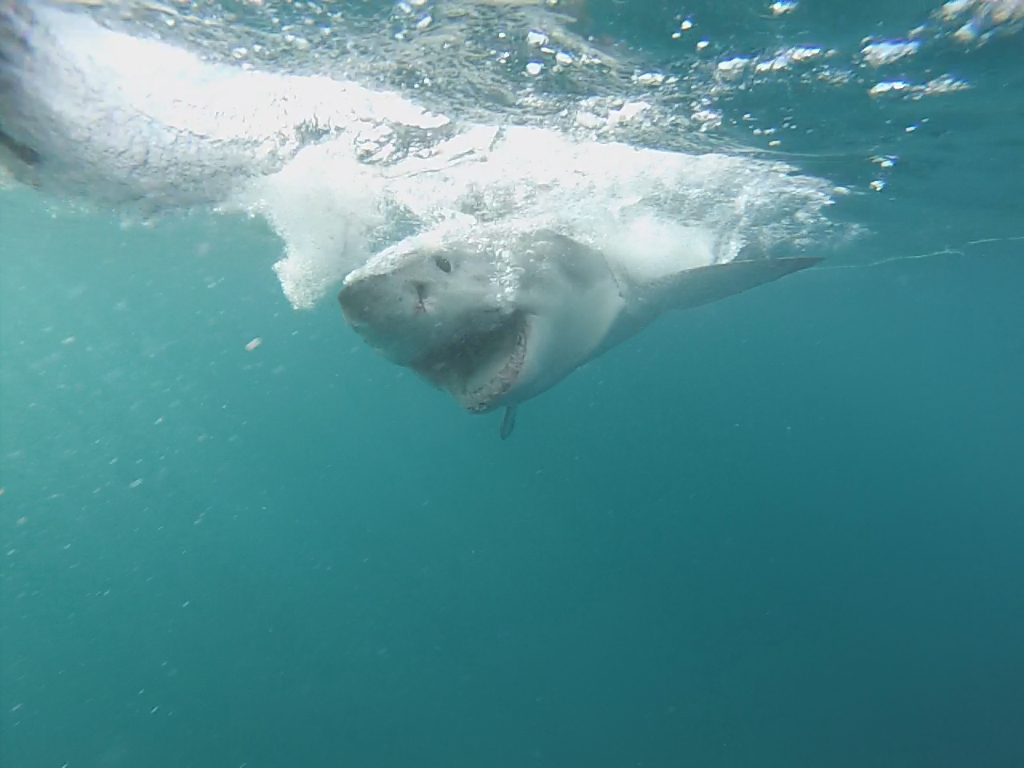 From inside the shark cage!
From inside the shark cage!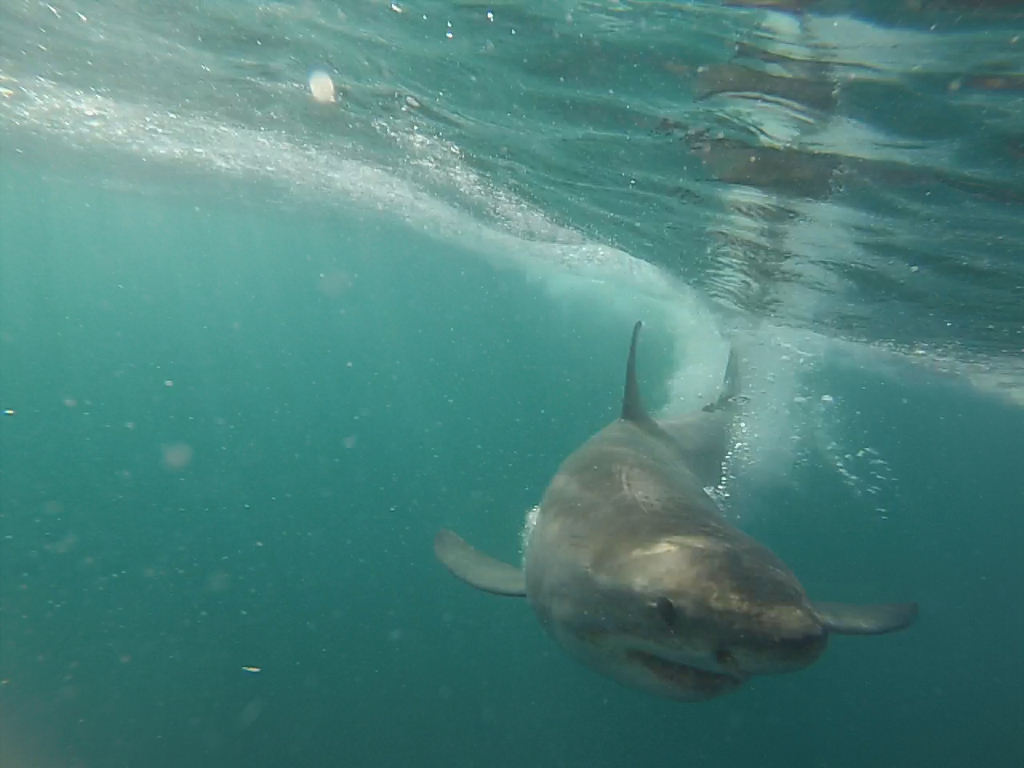 Still safely in the cage.
Still safely in the cage.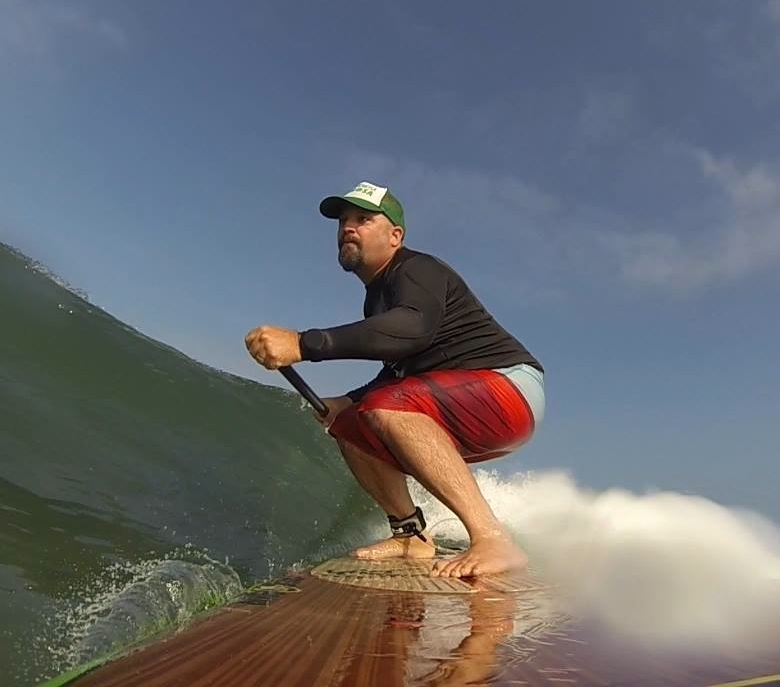
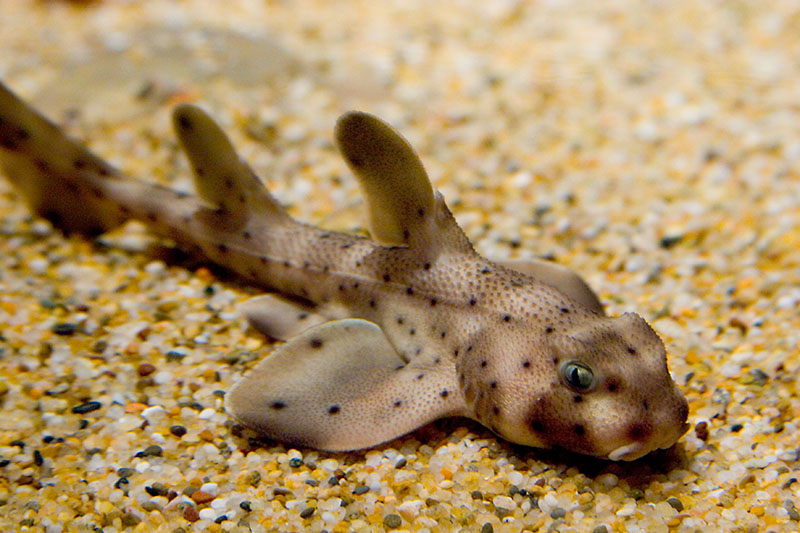 I cannot imagine what that little shark thought about its first kiss — but I loved it. I won’t do it again. I promise to hold back, because honestly I’m pretty sure that horn shark was pretty upset about the whole incident. So I encourage you to love sharks as much as possible but try to restrain yourself when you feel a “Kiss Attack” coming on. If you are in need of your shark “fix” then I very much encourage you to visit us at the Santa Monica Pier Aquarium, where you’ll get an up close encounter with horn sharks, swell sharks and leopard sharks. See you soon and feel free to ask for me by name — the Shark Kisser!
I cannot imagine what that little shark thought about its first kiss — but I loved it. I won’t do it again. I promise to hold back, because honestly I’m pretty sure that horn shark was pretty upset about the whole incident. So I encourage you to love sharks as much as possible but try to restrain yourself when you feel a “Kiss Attack” coming on. If you are in need of your shark “fix” then I very much encourage you to visit us at the Santa Monica Pier Aquarium, where you’ll get an up close encounter with horn sharks, swell sharks and leopard sharks. See you soon and feel free to ask for me by name — the Shark Kisser!