With some much-needed rain pelting the region, we pause to share some quick answers to commonly asked questions about rain and pollution. The storm will surely create a lot of waste—both in the form of trash on the beach and squandered opportunities to capture water in a time of drought.
I thought rain was a good thing. Why is Heal the Bay worried about it?
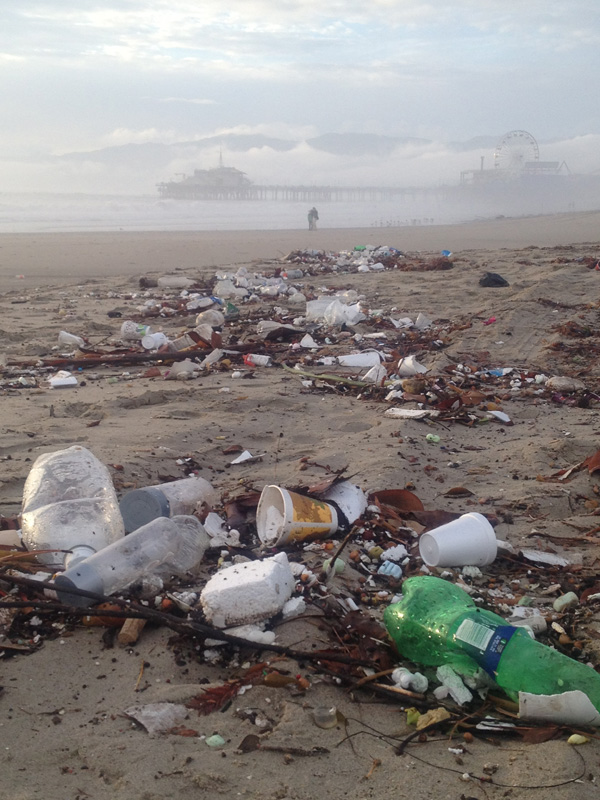

Yes, we desperately need rain in our drought-parched state. But rain creates urban runoff—the No. 1 source of pollution at our beaches and ocean.
How does rain create pollution?
Rimmed by foothills and mountains, Los Angeles County is like a giant concrete bowl tilted toward the sea. When it rains, water rushes along paved streets, picking up trash, fertilizer, metals, pet waste and automotive fluids before heading to the ocean via the region’s extensive stormdrain system.
Were stormdrains designed to trash the beach?
With memories of historical deluges on their minds, engineers designed L.A. County’s 2,800-mile stormdrain system in the ‘30s and ‘40s to prevent flooding first and foremost. Moving stormwater out to sea quickly was their top priority. But it also has the unintended function of moving trash and bacteria-laden runoff directly into the Santa Monica and San Pedro Bays, completely unchecked and untreated.
What is the economic impact of all that pollution?
People make nearly 50 million visits to Santa Monica Bay beaches each year. And the coastal economy in Los Angeles County generates more than $20 billion in goods and services each year. Polluted water and debris-laden beaches put these economic drivers at risk.
How much runoff results from a big rain?
An average one-inch storm will create about 10 billion gallons of runoff in L.A. County stormdrains. That’s 120 Rose Bowls’ worth of dirty water.
What is “stormwater capture” and why is Heal the Bay so excited about it?
The L.A. region now imports more than 80% of our water from Northern California and the Colorado River watershed, using enormous amounts of energy and capital to do so. In an era of permanent drought, we simply must do a better job of using the water we already have. We need to build innovative infrastructure projects that capture and reuse stormwater instead of sending it to senselessly pollute our seas. Runoff—if held, filtered and cleansed naturally in groundwater basins—can provide a safe source of water for human use.
What is the potential for reusing stormwater? How much water are we talking about?
A recent NRDC report found that capturing stormwater runoff for water supply across urban areas in Southern California and the San Francisco Bay Area could increase local water supplies by between 420,000 and 630,000 acre-feet per year, or roughly the same amount of water used by the entire City of Los Angeles on an annual basis.
What are examples of stormwater capture?
On a bigger scale, municipalities can develop multi-benefit wetlands, parks and open spaces that can capture and recharge groundwater supplies. Reclaimed stormwater can irrigate neighborhood parks, ball fields and school grounds instead of fouling rivers and beaches. On the individual lot level, property owners can equip homes with rain barrels and cisterns and redirect gutter flows into planter boxes. Under the County’s new stormwater regulations, new and redevelopment projects throughout the region are now required to retain the first ¾” of precipitation that fall on properties, instead of allowing it to run off into streets and ultimately the sea.
What does all this runoff to do the ocean and the animals that call it home?
Tens of thousands of marine animals die each year from ingesting trash or getting entangled in manmade debris. Seawater laden with chemicals and metals makes it harder for local marine life to thrive and reproduce.
What about the human health impacts?
Beachgoers who come in contact with polluted water face a much higher risk of contracting illnesses such as stomach flu, ear infections, upper respiratory infections and skin rashes. A UCLA epidemiology study found that swimmers are twice as likely to get sick from swimming in front of a flowing storm drain than from swimming in open water.
How can ocean lovers stay safe after a storm?
- Wait at least 72 hours before entering the water. Five days may be more appropriate at beaches near storm drains.
- Stay at least 100 yards away from storm drains, piers and enclosed beaches with poor circulation.
- Go to Heal the Bay’s Beach Report Card to get the latest water quality grades and updates.
What can I do in my daily life to reduce the impact of runoff-related pollution?
- Say NO to “convenience trash.” By purchasing fewer disposable goods, you’ll decrease the amount of plastic packaging and food wrappers that end up in the ocean. You’ll also save money!
- Dispose of trash properly. Keeping trash out of the street keeps trash out of the sea. Cigarette butts, fast food packaging and plastic bottles are the most frequently found items at our beach cleanups. And remember to pick up after your pet to keep bacteria out of our sea.
- Rip up your lawn. Nearly half of our water is used to care for our lawns. Not only is it a waste of water in an arid climate, it contributes to poor water quality due to pesticide and fertilizer runoff.
- Keep rainwater onsite. Many cities offer rebates to homeowners who install rain barrels or cisterns, which capture and infiltrate rainfall for later use around the home and garden.
How can I support Heal the Bay’s efforts to make L.A. smarter about stormwater?
- Come to a volunteer beach cleanup to spruce up a beach near you. Invite family and friends and win prizes!
- Follow us on social media to learn about our work and share information with your networks.
- Become a member. Your donation will underwrite volunteer cleanups, citizen science programs and lobbying and advocacy efforts by our science and policy team to develop more sustainable water policies throughout Southern California.
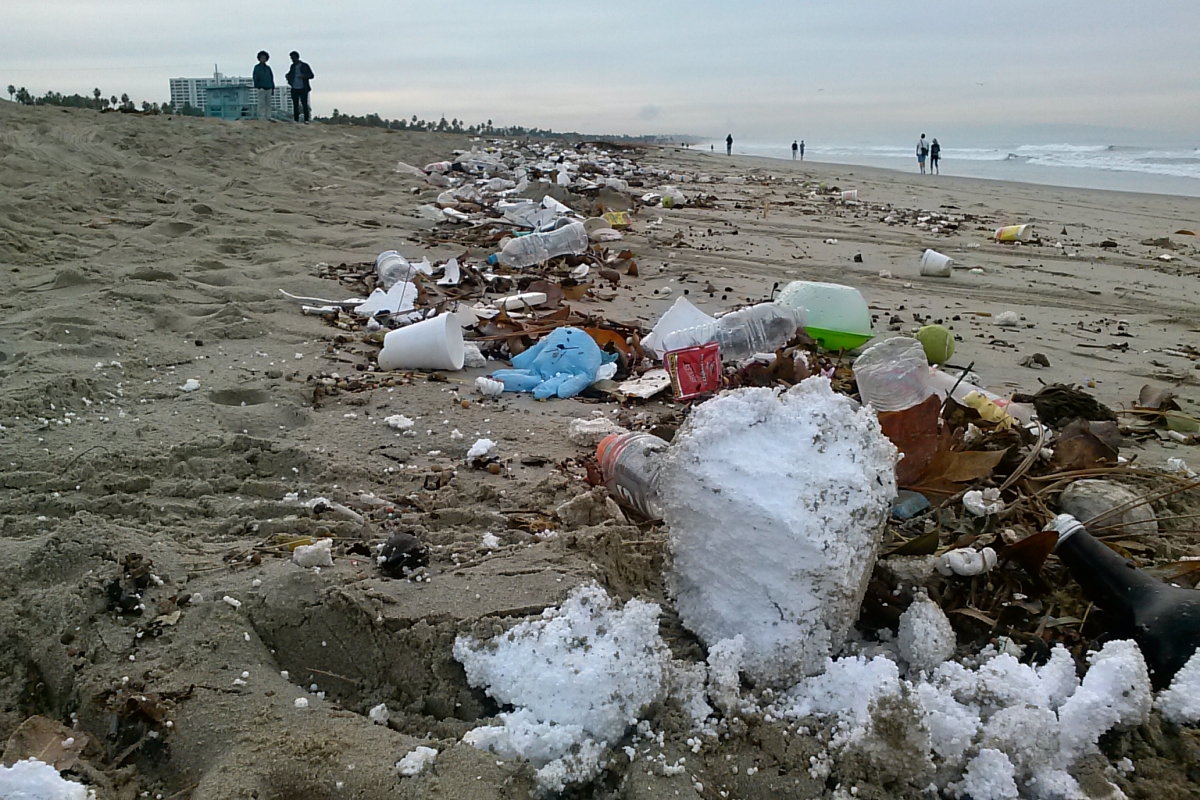



 Sad but true: the beach after heavy rain at the Pico Kenter storm drain
Sad but true: the beach after heavy rain at the Pico Kenter storm drain

