Local college students keep residents safe by conducting bacterial tests at freshwater sites throughout L.A. County.
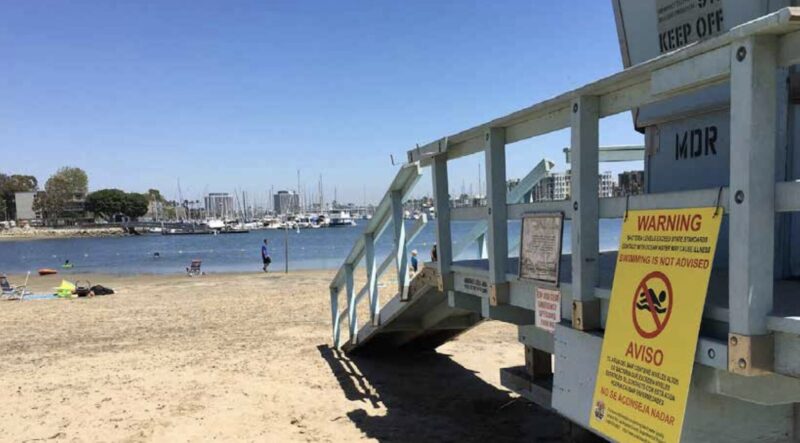
The entire greater L.A. watershed – from the mountain to the sea – is all connected. The health of the ocean cannot be separated from the health of the inland waterways that feed it. Unfortunately, despite the popularity and heavy use of freshwater recreation sites throughout the state, there is still not a comprehensive statewide water quality monitoring or notification program like we have for ocean beaches.
That’s where Heal the Bay’s Stream Team steps in – powered by local students.
Protecting the public from potentially harmful water has been Heal the Bay’s mission for the past 30 years with the Beach Report Card. Inland neighborhoods deserve the same public health information that coastal communities have.
To meet the needs of those communities, Heal the Bay monitors water quality at 35 inland freshwater recreation sites in greater L.A. Our science and policy staff analyze samples taken from local creeks, rivers, swimming holes and storm drains for fecal indicator bacteria, which can cause a number of serious illnesses.
We are fortunate to have the assistance of 14 students from regional colleges and universities help us gather samples and report findings. This year’s Stream Team members are helping monitor 12 inland freshwater sites this summer, all within the greater Los Angeles area, from Sepulveda Basin to Long Beach and Malibu Creek State Park.
Now in its sixth year, the Stream Team program this summer welcomes students from California State University Long Beach, Los Angeles Trade Technical College, California State University Los Angeles, UCLA, UC Santa Barbara and UC Santa Cruz.
We are committed to giving students professional work opportunities. We focus on providing practical experience in environmental fieldwork and laboratory analysis, increased exposure to database entry and management and development of communication and outreach experience. Summer interns also learn best practices for engaging with community members and stakeholders to promote environmental awareness.
Stream Team members are in charge of sampling at their assigned sites and carefully transporting the samples back to their respective laboratories. Students are tasked with processing these samples, where they incubate for 24 hours. The next day, students assess the samples and determine levels of total coliforms, E. coli and enterococci.
Using these results along with testing results from Los Angeles Sanitation in the L.A. River Recreation Zones, students assess a total of 35 freshwater sample sites and calculate A+ through F letter grades, using the newly implemented grading system introduced last season. You can read about the latest River Report Card and an analysis of greater L.A.’s cleanest and most problematic freshwater recreation areas here.
These grades, assembled by several Stream Team members, are displayed on Heal the Bay’s River Report Card website, which is updated weekly throughout the summer (June to September).
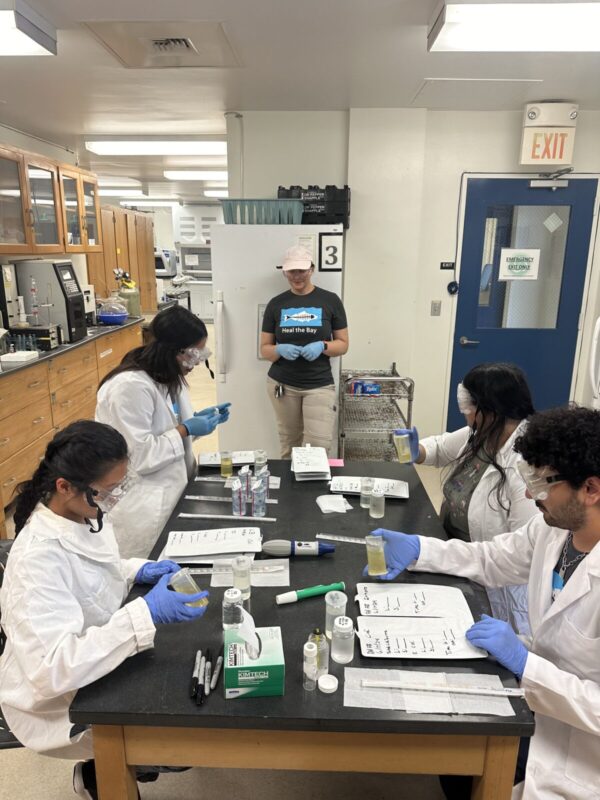
- After collecting samples at freshwater sites, students head to the lab to process these samples. Students from CSULB lab from left to right: Ellie Garcia, Emily Uy, Danny Herrera, Vina Rosa, and Zaria Alam.
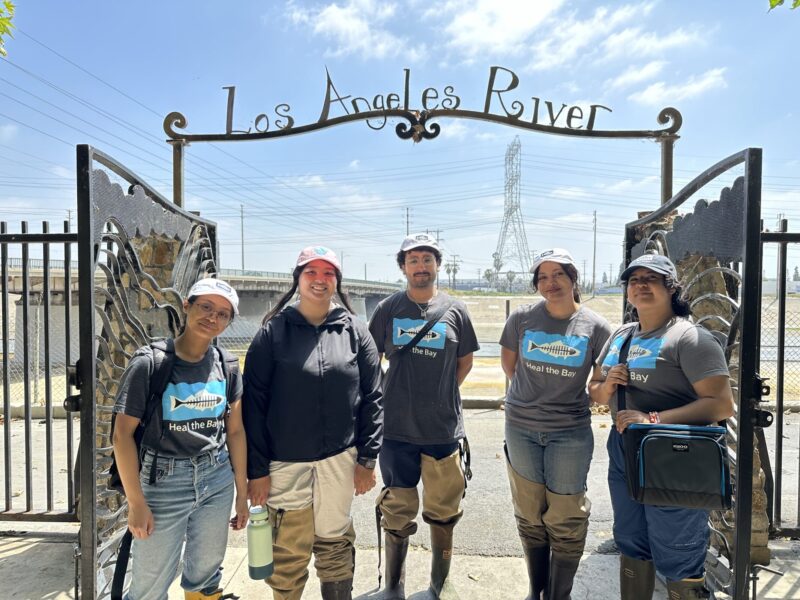
- Stream Team members stand outside one of the gates to enter the Los Angeles River. Left to right: Vina Rose, Emily Uy, Danny Herrera, Zaria Alam and Ellie Garcia.
As part of their work, Stream Team members were recently asked to share their experiences regarding the start of the 2024 sampling season. Some returning students have been working with Heal the Bay for several years. Some new students are joining the program for the first time.
Expectations vs First Impressions
Lyanne Fernandez: “Malibu Creek looked as expected but parts of the L.A. River vary greatly from site to site in ways that I did not expect. I never imagined how some parts of it look like a real, natural river.
Kate Medrano: “I had never actually visited the L.A. River, only seen it from a distance. I always just imagined it to be dirty and contaminated water, now I realize how much wildlife it contains and how diverse it really is.”
Sanam Viliani: “Before working for Heal the Bay, I had never visited the L.A. River, having only seen the creeks and drainage systems closer to the ocean. I expected the L.A. River to look similar, but I was surprised to find it had much more vegetation than I had imagined.”
- Returning students notice changes in sampling sites compared to last season. Vina Matias pictured above preparing to sample at the Compton Creek site in the Lower LA River.
- Stream Team members collect a sample at a section of the LA River at Willow St that is completely channelized.
A Future for Freshwater
Vina Matias: “Water is important for many aspects of life for both humans and animals. It’s required for living organisms to function, it can serve as habitats, it supports recreational activities, and so on. River monitoring contributes to the health of rivers because the data shows us their current status… With the data collected, we can understand how current policies and protocols are having an impact. Additionally, this data can help support the need for a plan of action to improve and protect our water sources… The data we collect is the starting point for action.”
Danny Herrera-Lopez: “This work is crucial for the community and environment because not only does it give us tangible evidence of pollution occurring all along the L.A. River but it also helps educate the population and locals on how we personally are being affected and how local wildlife is affected.”
Vicente Villaseñor: “Our work with the Summer Stream Team contributes to the understanding and protecting local water resources through education. Our findings of each site showcase to the public the levels of water quality, and by doing so, we are informing the public about the inherent risk that comes with natural bodies of water, whether that is through the L.A. River or the Pacific Ocean. There are always risks with local water resources, and we only try to provide information for their own sake. This is critical for the community and the environment that there is a group actively supporting groups of people’s use and access to clean safe water.”
- Stream Team members at Oso Park, on their first day of sampling. Left to right: Sanam Viliani, Lyanne Fernandez, David Martinez, Kate Medrano, Blaire Edwards and Vicente Villaseñor.
- Stream Team members watch as samples are taken at Rock Pool, part of the Malibu Creek watershed. Left to right: Annelisa Moe, Thais Arata, Amy Flores and Alex Miranda.
Our River Report Card aims to keep summer stream-goers safe and informed about water quality. Through consistent efforts, Heal the Bay hopes to create substantive and lasting change in how the L.A. River is managed so that all Angelenos can have equal access to safe and clean freshwater.
Our work would not be possible without the contributions of our team of students: Amy Flores, Vina Rose Matias, Lyanne Fernandez, Danny Herrera-Lopez, Thais Arata, Vicente Villasenor, Kate Medrano, Sanam Viliani, Emily Uy, Ellie Garcia, Zaria Alam, Alejandra Miranda, David Garcia and Blaire Edwards.
Before you explore our watershed this summer, remember not to swim for up to three days after a rain event, and check the River Report Card before you go. By making informed decisions, we can keep ourselves and our community safe.
Support our River Report Card and Stream Team Program with a $30 donation today!
Donate