
Through the end of December, we will share the stories of amazing people whose lives have been changed by Heal the Bay. Now they are changing our region for the better. Please make your Year-End Gift today to support the work of these water warriors.
Ken Seino almost died surfing at Malibu’s fabled First Point. First he was scared, then he was angry. Then with Heal the Bay’s help he took matter into his own hands – flying to Sacramento with us in 2009 to fight successfully for stricter pollution limits. Here’s his story in his own words:
Call me biased, but from the first time I surfed the place, I knew Surfrider Beach was special – dare I say sacred? But the continuous human pollution from Malibu Creek eventually played Russian Roulette with me and it won. I suffered a prolonged illness from a fecal virus contracted surfing here and I almost died from it. The disease damages the heart muscle and even causes your own immune system to weaken you. It is irreversible.
Two surfer friends of mine did die from the very same virus here. They asked me to help them fight for its restoration to the pure and holy place that the Chumash tribe ascribed it to be. In order to honor my friends and honor this place, how could I refuse?
As a member of the Malibu Surfing Association and a Surfrider Beach regular since 1971, I was asked by MSA president Michael Blum to accompany the “A-Team” to Sacramento and speak before the State Water Board.
The State Board was weighing in on whether to support the Regional Water Board’s earlier prohibition of on-site wastewater plants in the Malibu Civic Center area. Opposition to the action was strong with Malibu’s city attorney actually threatening litigation if the State Board upheld the prohibition, which aimed to prevent seepage of harmful bacteria from outmoded septic tanks.
I had heard of last-minute strategies by the city of Malibu to have the septic ban remanded to the L.A. Board because of its contention that the prohibition was “technically unfeasible and politically unachievable.”
So I was worried as I walked into the State Water Board hearing room and sat next to my esteemed teammates. We each spoke, with [former HTB president] Mark Gold wrapping up succinctly all of the issues at stake. We sat down, hoping and praying that our words persuaded the five-member board that would make the final decision.
The city of Malibu arrived with its own A-Team. Euphemized threats of litigation were uttered and Mark Gold was gratuitously misquoted. I hoped that the board would see through this. Other opponents spoke as well. The residents and commercial interests complained how oppressive the ban would be to them personally.
But suddenly, after the last speaker had appealed, the board called for the vote. And in a few minutes, a unanimous vote (5-0) in our favor was recorded. About 90% of the room vacated as the board moved on to other business. We sat there together silent, staring straight ahead, stunned. All these decades of activism, protest and creation of organizations to fight this breach upon the environment and public health, and now the victory had finally been achieved. Is this how it felt at Waterloo? Mark Gold got up from his chair, looked at us and said, “What, did someone die? Hey, we won!”
It didn’t hit me personally until I was on the plane staring out the window as we were coming home. I thought about my own fight for this place I love, and also about Ralph Gambina and Erik Villanueva who died from infections from surfing Malibu. They were vocal in insisting upon this ban of septic tanks in Malibu. This is what they fought for and it is finally a reality. As I stared out the window of the plane at the glistening ocean, I cried for Malibu, but this time they were tears of joy.
Make a Year-End Gift to Heal the Bay
Our work isn’t possible without the real passion, action and commitment from people like Ken and you. Help us spark more positive change in our region, up and down the coast, and around the world.
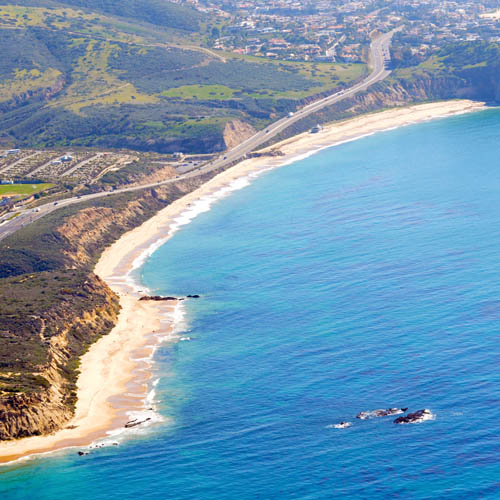
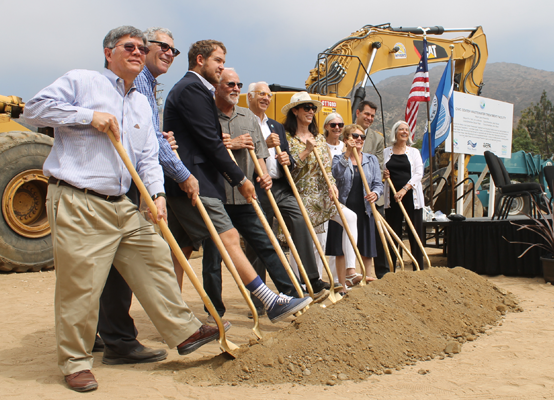














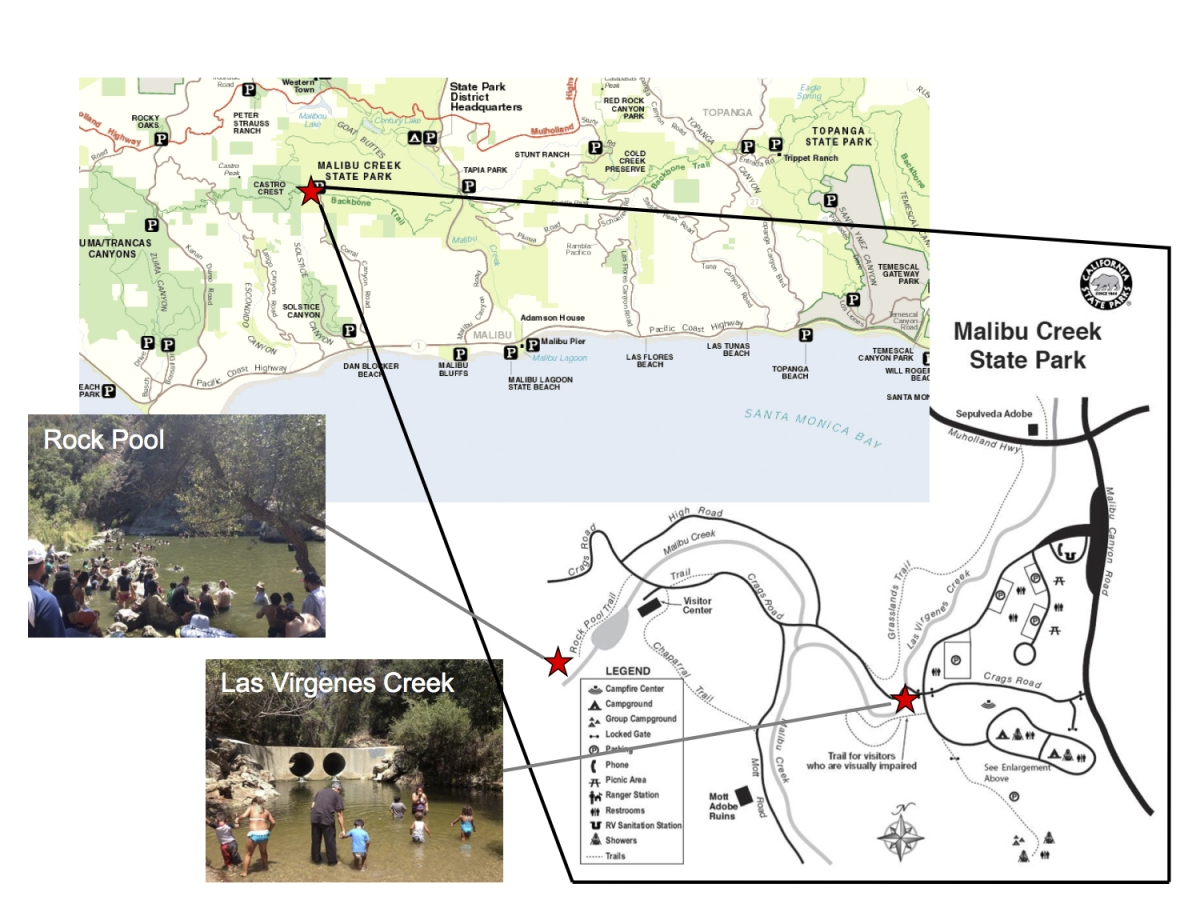
 It was especially gratifying to see Mark Gold, past Heal the Bay president and current board member, in attendance. Amid often fierce opposition from city officials and some Malibu property owners, Gold led the charge to demand an end to septic tanks in the Civic Center area for many years. He helped broker an MOU between the city and the regional water board that phased out septic tanks and mandated the building of a more modern treatment facility. (You can read more about his war wounds in one of his blog posts
It was especially gratifying to see Mark Gold, past Heal the Bay president and current board member, in attendance. Amid often fierce opposition from city officials and some Malibu property owners, Gold led the charge to demand an end to septic tanks in the Civic Center area for many years. He helped broker an MOU between the city and the regional water board that phased out septic tanks and mandated the building of a more modern treatment facility. (You can read more about his war wounds in one of his blog posts 



 It’s too bad the questionable water quality haunts the minds of most surfers at Malibu, which is why California Swimmable Day is important – it reminds us that all beaches should be safe for swimming, and that clean-up efforts at dirty beaches need to be implemented to meet this goal. Sometimes it’s hard to stay out of the surf after a rain, especially with a nice storm swell, but the risk versus reward has to be weighed.
It’s too bad the questionable water quality haunts the minds of most surfers at Malibu, which is why California Swimmable Day is important – it reminds us that all beaches should be safe for swimming, and that clean-up efforts at dirty beaches need to be implemented to meet this goal. Sometimes it’s hard to stay out of the surf after a rain, especially with a nice storm swell, but the risk versus reward has to be weighed.