Reflecting on a Year of Progress
Heal the Bay achieved significant accomplishments in 2023 in safeguarding our waters, preserving biodiversity, and raising awareness about the importance of environmental conservation. Through our collective efforts and with your unwavering support, we worked tirelessly to create cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable coastal waters and watersheds for Los Angeles and beyond from summit to sea. As we reflect on the achievements of this past year, we are thrilled to carry this momentum into the coming year, always aiming to make a lasting difference. Celebrate them with us!
2023 Highlights

Our expertise was sought after, and our work was celebrated.
In 2023, Heal the Bay was honored for decades of commitment to the environment.
- The City of Los Angeles officially declared October 20, 2023 “Heal the Bay Day in LA” in recognition of nearly four decades of accomplishments including the 20th anniversary of our Angler Outreach Program as well as our Aquarium.
- The 3rd Annual Heal the Bay One Water symposium was convened at Will Rogers State Beach, establishing Heal the Bay as a thought leader among civil engineers, water conservation experts, and local, county, and state legislators.
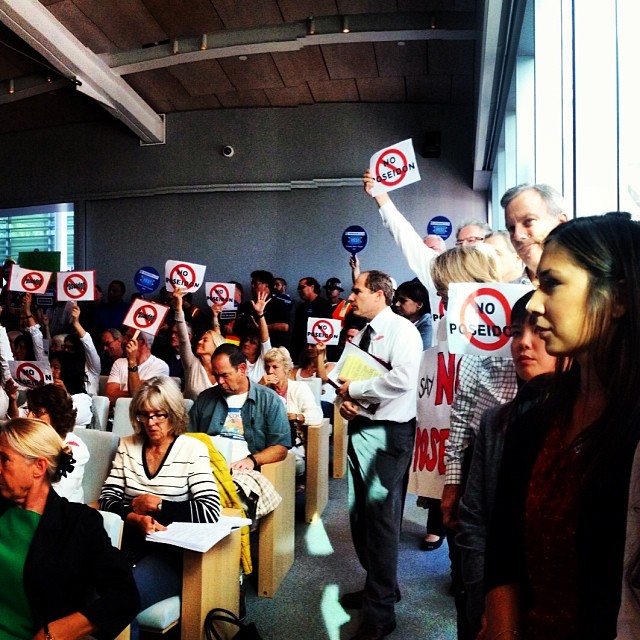
- Heal the Bay was officially appointed to the LA 28 Environmental Sustainability Committee for the 2028 Summer Olympics.
- Heal the Bay Aquarium celebrated its 20th anniversary with an official ribbon-cutting of a new Welcome Center located on top of the historic and iconic Santa Monica Pier.
The future of our planet starts with better environmental policy.
Heal the Bay played a pivotal role in successfully advancing policies and legislation for the benefit of water quality, affordability, and coastal ecosystems to ensure a more sustainable Los Angeles region and climate-resilient California.
- Heal the Bay, co-sponsored Assembly Bill 1572 (Friedman) alongside the NRDC and the Los Angeles Metropolitan Water District. This new law bans the use of drinking water to irrigate non-functional (purely ornamental) turf on governmental and commercial landscapes; and is expected to save the equivalent amount of water that 780,000 households use in a year.
- Heal the Bay advocated for water quality protection at the Boeing Santa Susana Field Laboratory site in Simi Valley. The Los Angeles Regional Water Board voted in October to keep regulations on surface water that flows from this previous industrial site, keeping stringent water quality limits, adding more monitoring, and addressing the potential for surface water pollution to impact groundwater, a huge win in the ongoing battle for water quality protection.
- Our policy team worked to legally strengthen and streamline fishing regulations to make fishery enforcement more equitable through Assembly Bill 1611 (Lowenthal). This new Heal the Bay sponsored law was supported by conservationists and fishery regulatory agencies alike as a win-win for both nature and the fishing community.
- Heal the Bay co-authored a new (and well-received) Vision 2045 Report and shared it with LA County decision-makers who are tasked with overseeing the ambitious Safe, Clean, Water Program (SCWP). This collaborative “vision” laid out a roadmap of bolder goals, and recommendations to more quickly and definitively reach 2045 SCWP targets.
It Takes a Very Large Village.

This year Heal the Bay published its first Volunteer Impact Report highlighting the accomplishments of our 22,017 volunteers from the 2022 season, which paved the way for the many volunteer successes of 2023.
- In 2023, Heal the Bay volunteers collected more than 22,000 pounds of trash and contributing 71,048 hours to protecting our precious watershed and coastal waters!
- In September, Heal the Bay mobilized 7,337 volunteers on Coastal Cleanup Day, removing 16,211 pounds of trash (including 429 pounds of recyclables) from greater Los Angeles coastlines and waterways.
- Heal the Bay’s work is powered by everyday heroes and Spectrum News highlighted one of our dedicated volunteers.
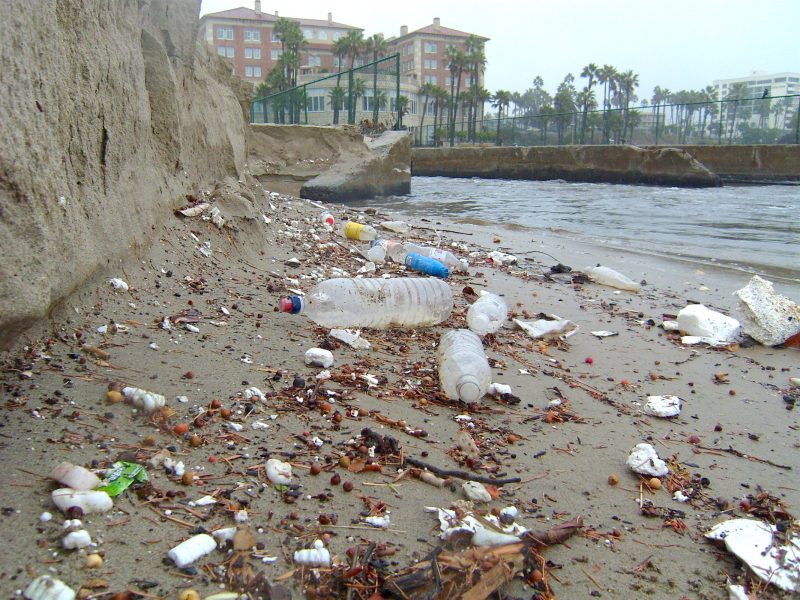
Sticking a Fork in Plastic at the Source
Recognizing the urgent need to combat plastic pollution, Heal the Bay continues impactful campaigns encouraging individuals and businesses to adopt sustainable practices. For several years, staff has been working with LA City and County to help create legislation aiming to break the harmful plastic cycle. By advocating for reducing single-use plastics and promoting responsible waste management, we took significant steps toward a plastic-free future.
- Our “No Bag November” campaign reaffirmed Heal the Bay’s commitment to a plastic-free Los Angeles. Through partnerships and community activations, No Bag November urged Angelenos to say “no” to single-use plastic bags and encouraged everyone to grab their reusable bags instead.
- In 2023, the implementation of THREE new laws made big waves for the environment as a means to reduce plastic in our oceans.
- As a leader in the Reusable LA Coalition, we co-launched the “Hold the Plastic, please,” campaign to educate businesses and the public about LA City and County plastic bans that Heal the Bay and partners advocated to pass.
Environmental Health IS Public Health
In 2023, Heal the Bay continued its relentless commitment to ocean water and freshwater quality from summit to sea.
- Since its launch in 2003, Heal the Bay’s Angler Outreach Program (in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency) has educated more than 190,000 anglers about which fish are contaminated, and which are safer to eat.
- Our annual Beach Report Card released this year remains the gold standard, providing access to the latest water quality information based on levels of fecal-indicator bacterial pollution in the ocean at over 700 beaches. For more than 30 years, our annual report has assigned “A-to-F” letter grades and ranked the “Best and Bummer” lists across beaches from Washington State to Tijuana, Mexico.
- The 5th annual River Report Card was also released, ranking freshwater quality and providing grades for 35 freshwater recreation areas in Los Angeles County tested during the summer of 2022. This summer we debuted our upgraded River Report Card with an intuitive letter grading system and celebrated the achievements of our 2023 Summer Stream Team. These two programs are at the forefront of our efforts to keep LA’s waters safe and enjoyable for all.
Conservation and Marine Protection Are Key to Our Mission

Heal the Bay reaffirmed its commitment to biodiversity through both volunteer activations and the tireless efforts of our husbandry, operations, and education Aquarium teams.
- Heal the Bay Aquarium plays a pivotal role in species conservation through research, breeding programs, and public awareness campaigns. In 2023, sixteen fish, three swell sharks, and dozens of moon jellies were born at the Aquarium; and our animal care team released five species of protected and rehabilitated marine life including a keystone species, the California Sheephead fish, and a critically endangered Giant Spotted Bass into the Santa Monica Bay. By releasing these animals back into the wild, Heal the Bay continues its mission to protect and support the biodiversity of wild fish populations.
- As part of our collective commitment to successful conservation efforts, Heal the Bay Aquarium officially joined the Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA) Wildlife Trafficking Alliance. As an official member of US Fish & Wildlife Department’s Wildlife Confiscation Network pilot program, the aquarium is certified to care for the well-being of wildlife confiscated from illegal trade.
- Heal the Bay’s Science and Policy Team successfully advocated for state funding to research DDT in 2022-23 and is now working as part of a coalition to lead public meetings and educate Californias on the impacts of DDT on public health and biodiversity.
- As a watchdog for Marine Protected Areas, Heal the Bay’s MPA Team is actively contributing and analyzing critical data on California’s first decade-long review that began in 2023. One of the biggest conclusions of the review highlighted the fact that protecting these precious estuaries for the past decade has worked, allowing for flourishing biodiversity, larger populations, and bigger individual animals in these safeguarded areas.
Environmental Justice is a pillar of environmental health.
This year Heal the Bay stood up to big oil and continued to advocate for communities that experience the worst systemic and often immediate impacts of environmental injustice and climate change.
- For decades Heal the Bay has advocated alongside organizations like Stand Together Against Neighborhood Drilling to oppose oil drilling in Los Angeles neighborhoods, a practice long seen as an environmental injustice and a public health crisis. In October of 2023, the LA County Regional Planning Commission voted in support of phasing out oil drilling in the Inglewood Oil Field, one of the largest neighborhood oil fields in the country.
- In 2023 Heal the Bay publicly endorsed the Campaign for a Safe and Healthy California and will work alongside public health groups, community and faith organizations, and environmental justice leaders from across California to “KEEP THE LAW” (SB 1137) on the November 2024 ballot. This law prohibits new oil wells within 3,200 feet of homes, schools, day care centers, parks, healthcare facilities, and businesses.
Environmental Education, Outreach and Sharing our Passion to Protect What We Love
Education remained a cornerstone of our mission. In 2023, Heal the Bay expanded our outreach program, teaching schools and communities to understand the importance of environmental conservation and the role each individual can play.
- Through innovative approaches and interactive science-based programs, educational efforts continued to inspire and inform diverse audiences. The Heal the Bay Aquarium field trip program sponsored 10,285 students from 22 school districts in LA County— 79% were Title 1 schools.
- This year, “Coastal Cleanup Education Day” at the Aquarium hosted more than 250 3rd-5th grade students from across Los Angeles County for a day of beach exploration, scientific excursions, pollution education, and hands on learning while having some fun in the sun.
- Heal the Bay Science Camp is an opportunity to foster a deeper connection with marine life in early educational development. In 2023, Spectrum News featured the program. There are still a few spots available January 2-5 “Extreme Winter” Science Camp. Register your future scientist here.
Cheers to 2023

As we look back on 2023, Heal the Bay celebrates a year of accomplishments, resilience, and collaboration. These achievements underscore the collective efforts of our dedicated team, volunteers, and supporters who made a positive impact on the health of our oceans and coastal ecosystems.
Here’s to a future filled with even greater strides toward a sustainable and thriving planet!
Looking to the Future with 2024 in our sights

In 2024, Heal the Bay will enter a bold five-year strategic plan with a focus on protecting and restoring the Los Angeles environment and water. The plan aims to improve water quality, increase access to clean water, and advocate for policies that benefit the environment. We have outlined specific goals and initiatives, such as reducing plastic pollution, restoring wetlands, and engaging communities in environmental education and action.
Thank you for all our supporters both past and present.