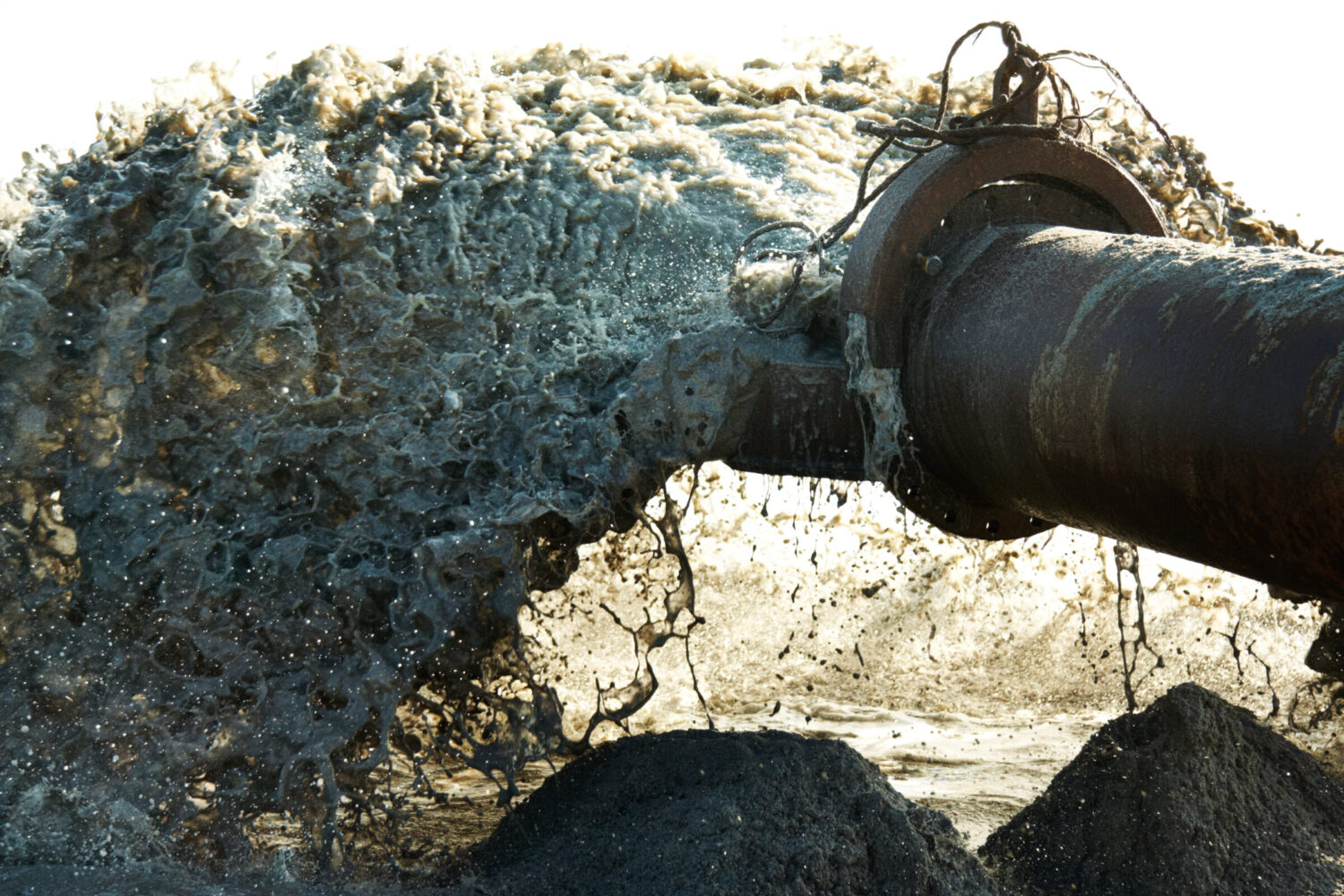

On March 26, in response to lobbying from the oil and gas industry, the federal Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced rollbacks on enforcement of regulations during the COVID-19 response. These rollbacks put public health at risk by letting industries off the hook for their legal requirements to control their pollution. Communities that are already disproportionately burdened by pollution, including the unsheltered and low-income communities of color, are the ones who will be hit hardest. The government’s response to a pandemic should not upend its commitment to address other, longstanding threats to public health.
It is clear that COVID-19 is having major impacts on all sectors, from individuals to small mom-and-pop businesses to large factories. There may be cases when a relaxation in requirements is acceptable to help those businesses, but to cease oversight altogether is not the answer. Blanket exemptions cannot be tolerated, because doing so puts people’s health further at risk, particularly those who are most vulnerable and most likely to be impacted by COVID-19. Any regulatory flexibility must be assessed on a case-by-case basis.
Now is not the time for blanket rollbacks of environmental regulations. The administration’s recent actions to rollback regulations on car fuel standards as well as water and air pollution are unconscionable and only take advantage of this terrible pandemic at the expense of public health.
What do the EPA rollbacks mean?
We have seen dozens of piecemeal rollbacks during this current administration. Now the EPA has released a memorandum announcing across-the-board rollbacks on enforcement of regulations that protect public health and natural resources, including clean water. It applies to any facility regulated by the EPA including private industries that discharge polluted water, as well as essential services including drinking water or wastewater treatment facilities.
The memorandum states that COVID-19 “may affect the ability of an operation to meet enforceable limitations on air emissions and water discharges, requirements for the management of hazardous waste, or requirements to ensure and provide safe drinking water.” The memorandum encourages facilities to report instances of non-compliance that may create an acute risk to human health or the environment. But encouragement is not enough – these occurrences must be reported immediately and publicly so that people are aware of the increased risks to their health.
Additionally, the EPA will no longer penalize violations of routine monitoring and other obligations. Monitoring and record keeping are fundamental to addressing pollution – knowing which contaminants (and how much) are discharged into our waterways allows us to prioritize public health issues and demand plans to address the pollution.
Here in California, state laws like the Porter-Cologne Act protect public health and the environment by creating a strong backstop to prevent environmental rollbacks; however, this federal non-compliance policy creates enormous pressure for state agencies to follow suit.
The California State Water Resources Control Board (State Water Board) announced back on March 20 that the “timely compliance by the regulated community with all Water Board orders and other requirements… is generally considered to be an essential function during the COVID-19 response.” However, they are reviewing requests to roll back protective measures related to water here in California, on a case-by-case basis. We are counting on the State Water Board to uphold environmental and public health protections, and provide leniency only when it is in the public interest.
What are people doing about these rollbacks?
As we all know, WATER IS LIFE. Particularly now, as we respond to COVID-19, we must ensure reliable access to safe and clean water, to protect the health of people and the natural resources on which we depend. Therefore, advocacy groups across the country have been fighting these rollbacks since they were first announced.
The Natural Resources Defense Council and a coalition of environmental justice, climate justice, and public interest advocacy groups filed a Petition for Emergency Rulemaking in response to this reckless non-enforcement policy, stating that any facility that stops monitoring and reporting their pollution must notify the EPA, to be publicly posted within one day.
Dozens of California based environmental groups (including Heal the Bay) sent a letter to Governor Newsom and many other state officials, urging them to remain committed to prioritizing public health and the availability of safe and clean water for all Californians.
Heal the Bay is urging the EPA and the State Water Board to uphold environmental regulations that protect public and environmental health, and to give leniency only when it is truly necessary and does not jeopardize public health. We also demand transparency so that any requests approved by the State Water Board are publicly noticed so the public can protect themselves and groups like Heal the Bay can continue to watchdog the decision-making process.
How you can help!
Sign Heal the Bay’s petition to tell our State Water Board to:
- uphold environmental regulations to protect public and environmental health,
- only give leniency when it is necessary and does not jeopardize public health, and
- ensure transparency so the public can know when any leniency is given.
Join the Center for Biological Diversity to fight the federal rollback by sending in your own comment letter directly to Andrew Wheeler (The Administrator of the EPA), or submit a letter to the editor of your local paper.




 Qué estamos haciendo: Protegiendo la salud pública a través de programas de educación científica y comunitaria sobre pesca y aguas contaminadas en playas y ríos de LA.
Qué estamos haciendo: Protegiendo la salud pública a través de programas de educación científica y comunitaria sobre pesca y aguas contaminadas en playas y ríos de LA. Qué estamos haciendo: Eliminando los desechos plásticos nocivos de nuestras playas y sistemas fluviales y restaurando la vitalidad de nuestro océano y cuencas hidrográficas.
Qué estamos haciendo: Eliminando los desechos plásticos nocivos de nuestras playas y sistemas fluviales y restaurando la vitalidad de nuestro océano y cuencas hidrográficas.

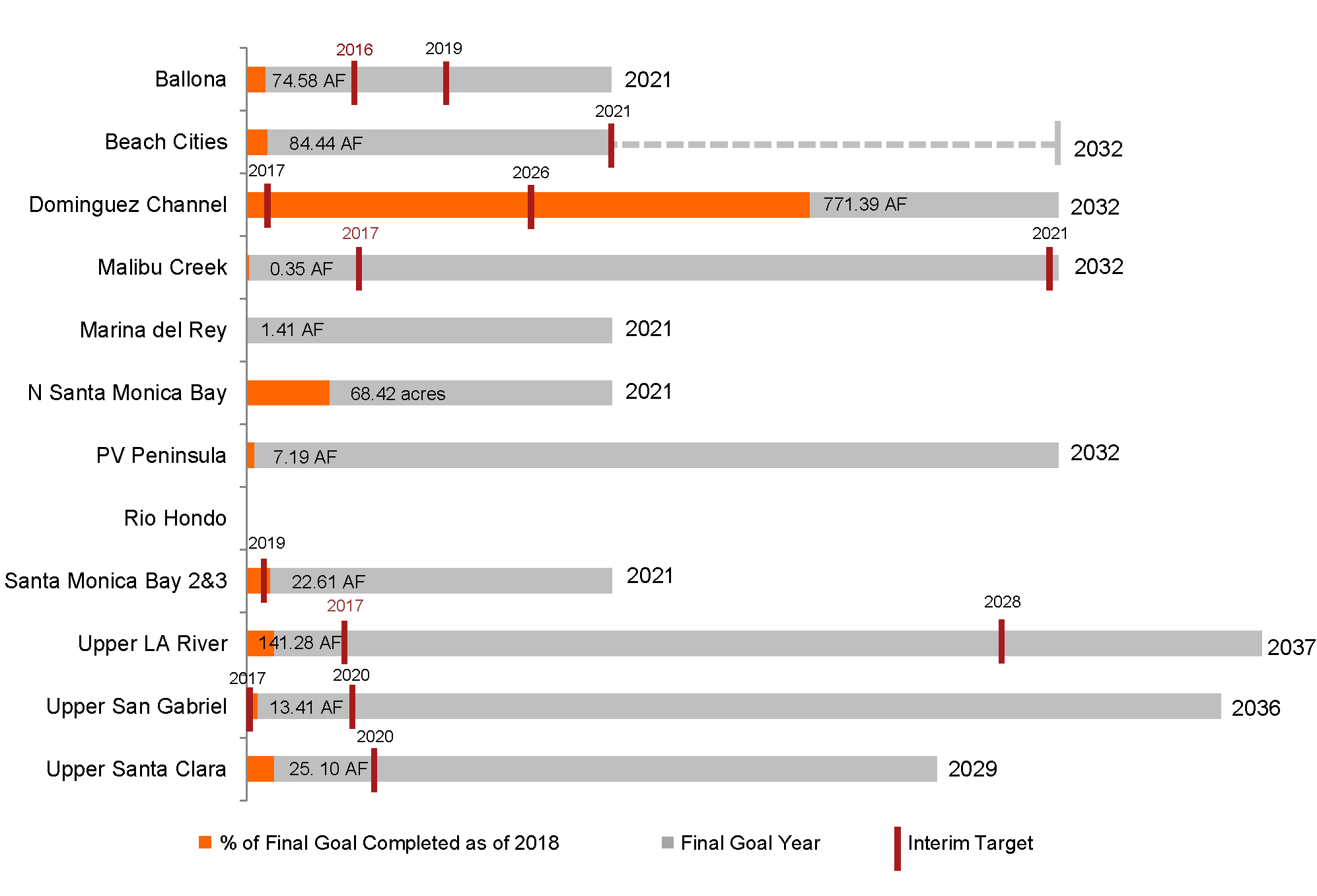 The graphic above is an overall aassessment of progress for each of the 12 watershed management groups, based on either total retention capacity in acre feet (AF) or total area addressed (acres). Each grey bar represents the final goal for each group, labelled with the final deadline to reach this goal. The orange portion of the bar represents the retention capacity of projects completed since the 2012 Los Angeles County MS4 Permit was approved, as a percentage of the total goal. Interim targets, when provided, are displayed with red vertical lines as a percentage of the total goal, and labeled with the relevant interim deadline year. A final goal was not provided in the Rio Hondo group, so progress cannot be displayed. Only an interim goal was provided in the Beach Cities group, so the final goal was uncertain, identified with a dashed line above.
The graphic above is an overall aassessment of progress for each of the 12 watershed management groups, based on either total retention capacity in acre feet (AF) or total area addressed (acres). Each grey bar represents the final goal for each group, labelled with the final deadline to reach this goal. The orange portion of the bar represents the retention capacity of projects completed since the 2012 Los Angeles County MS4 Permit was approved, as a percentage of the total goal. Interim targets, when provided, are displayed with red vertical lines as a percentage of the total goal, and labeled with the relevant interim deadline year. A final goal was not provided in the Rio Hondo group, so progress cannot be displayed. Only an interim goal was provided in the Beach Cities group, so the final goal was uncertain, identified with a dashed line above.
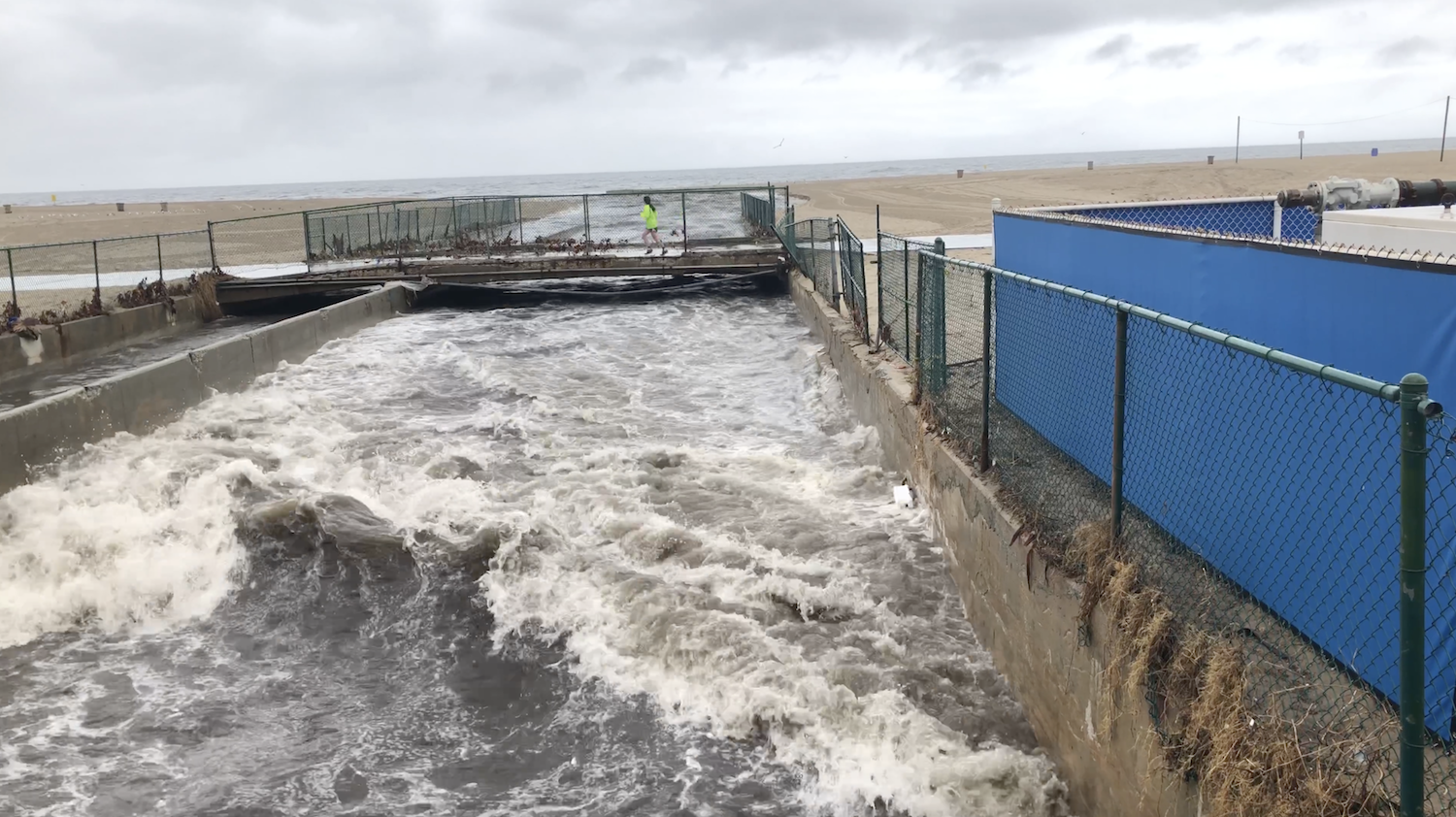
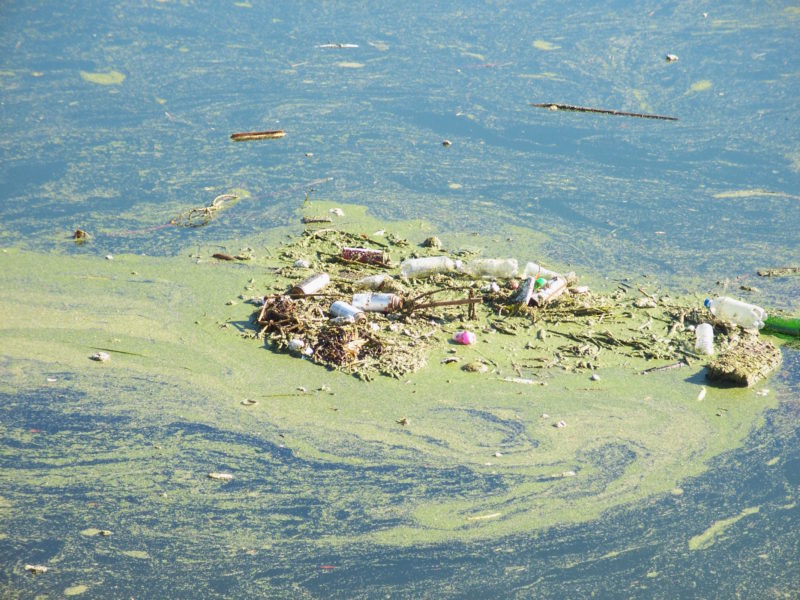
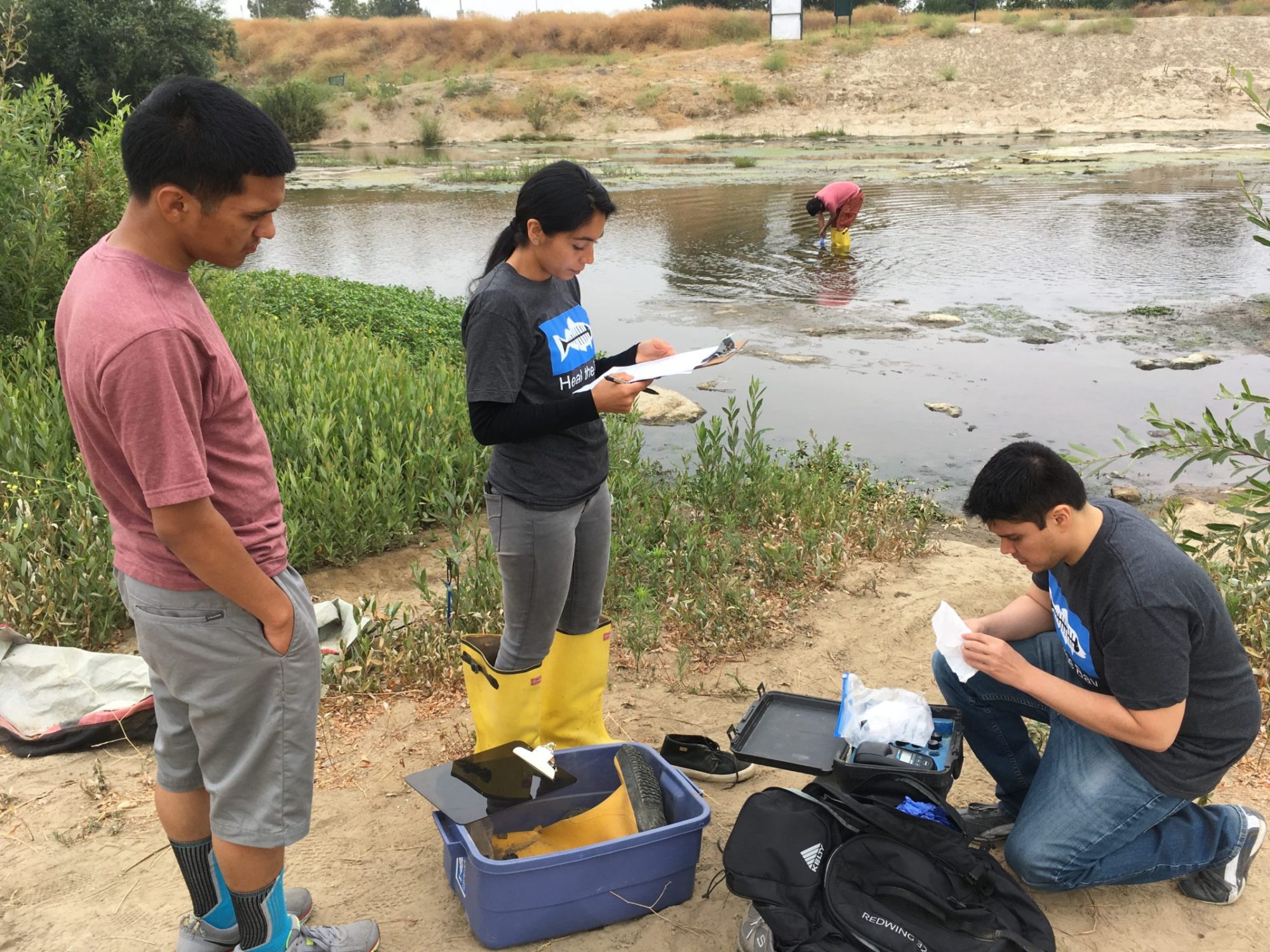

















 Las áreas acuáticas para nado y recreación en el condado de Los Angeles brindan oportunidades importantes para quienes disfrutan y valoran la naturaleza de nuestros ríos y arroyos. Desafortunadamente, existe poca información o notificación pública de la calidad del agua por parte del estado. Como resultado, carecemos de datos estandarizados y la información disponible para el público es mínima y difícil de interpretar.
Las áreas acuáticas para nado y recreación en el condado de Los Angeles brindan oportunidades importantes para quienes disfrutan y valoran la naturaleza de nuestros ríos y arroyos. Desafortunadamente, existe poca información o notificación pública de la calidad del agua por parte del estado. Como resultado, carecemos de datos estandarizados y la información disponible para el público es mínima y difícil de interpretar.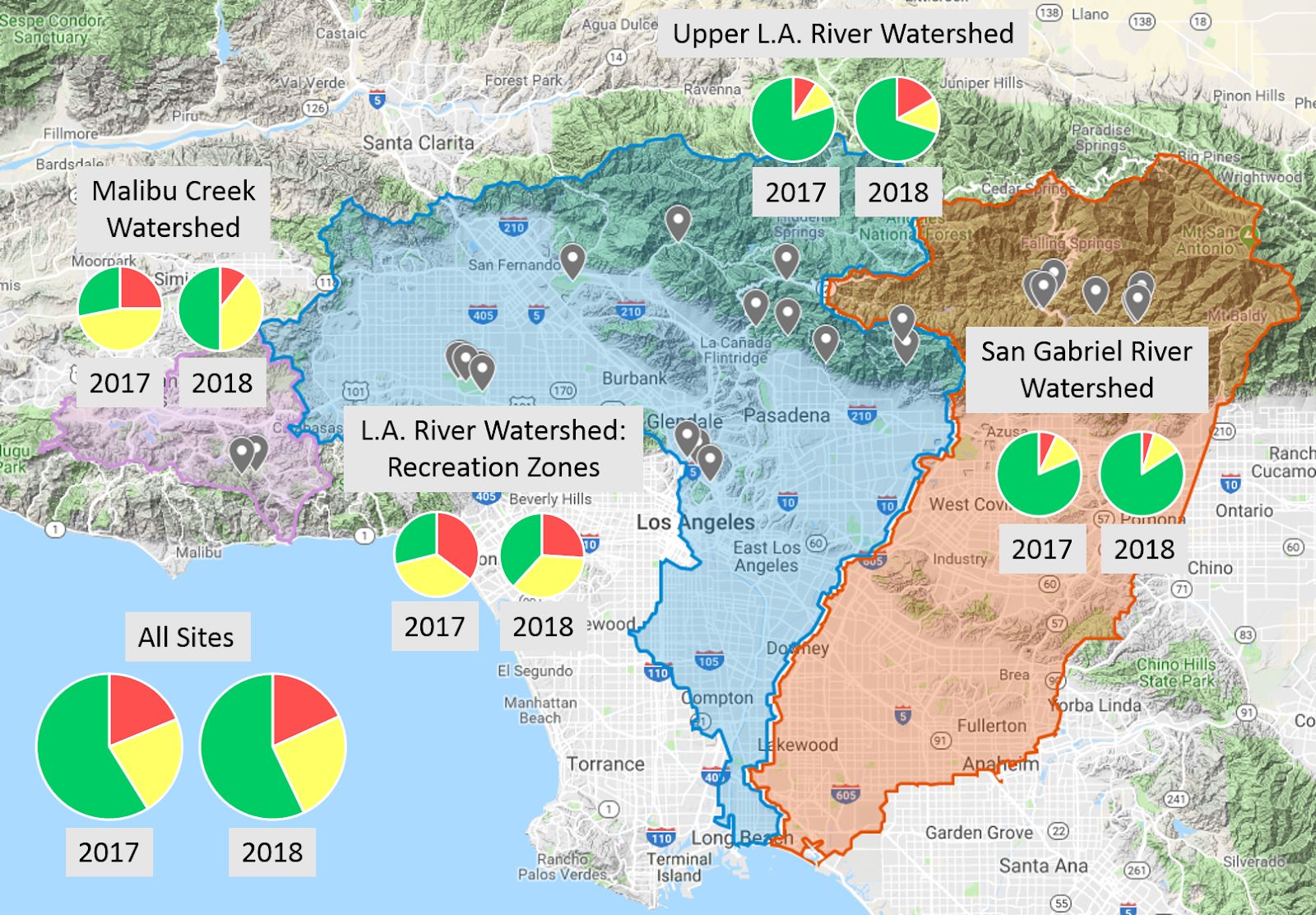
 Tips for enjoying and staying safe in L.A.’s rivers, streams, and creeks
Tips for enjoying and staying safe in L.A.’s rivers, streams, and creeks