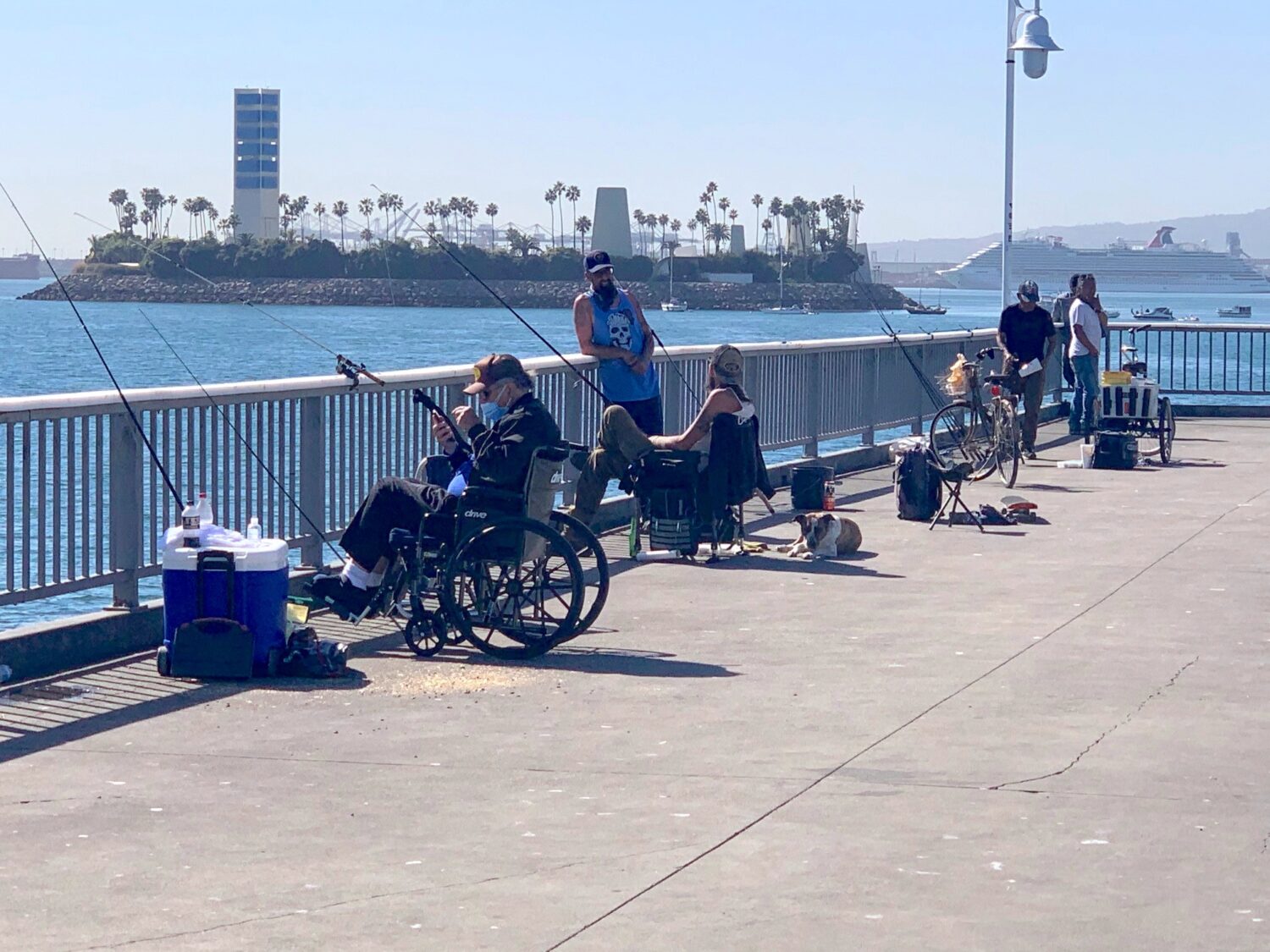
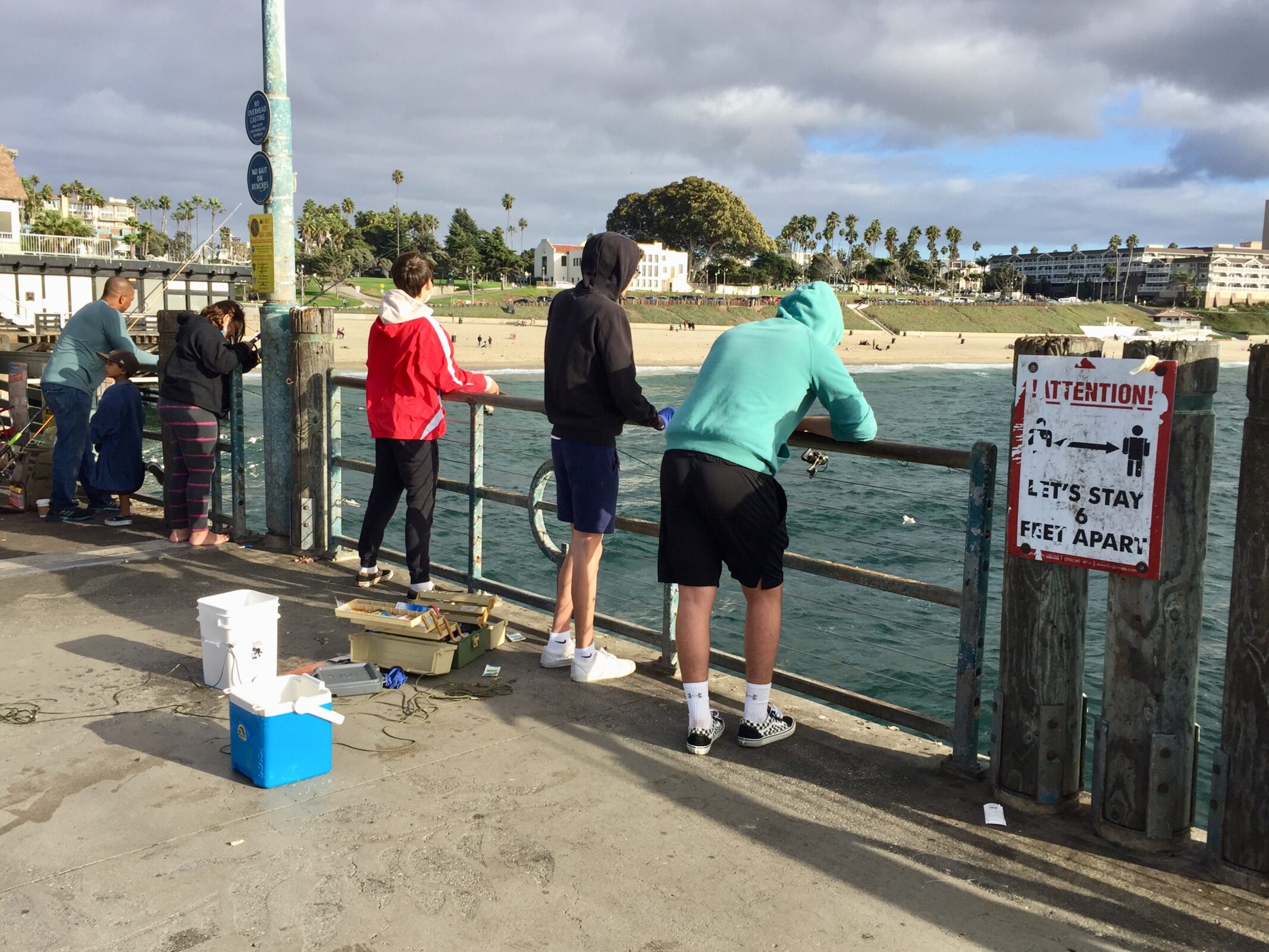
Belmont Veterans Memorial Pier está ubicado en Long Beach, cerca del vecindario Belmont Shore. El muelle actual se inauguró en 1967 y tiene 1.800 pies de largo. Al final del muelle, hay una gran área hexagonal con dos “alas” que se extienden 120 pies desde cada lado, lo que le da al muelle una forma de T general.
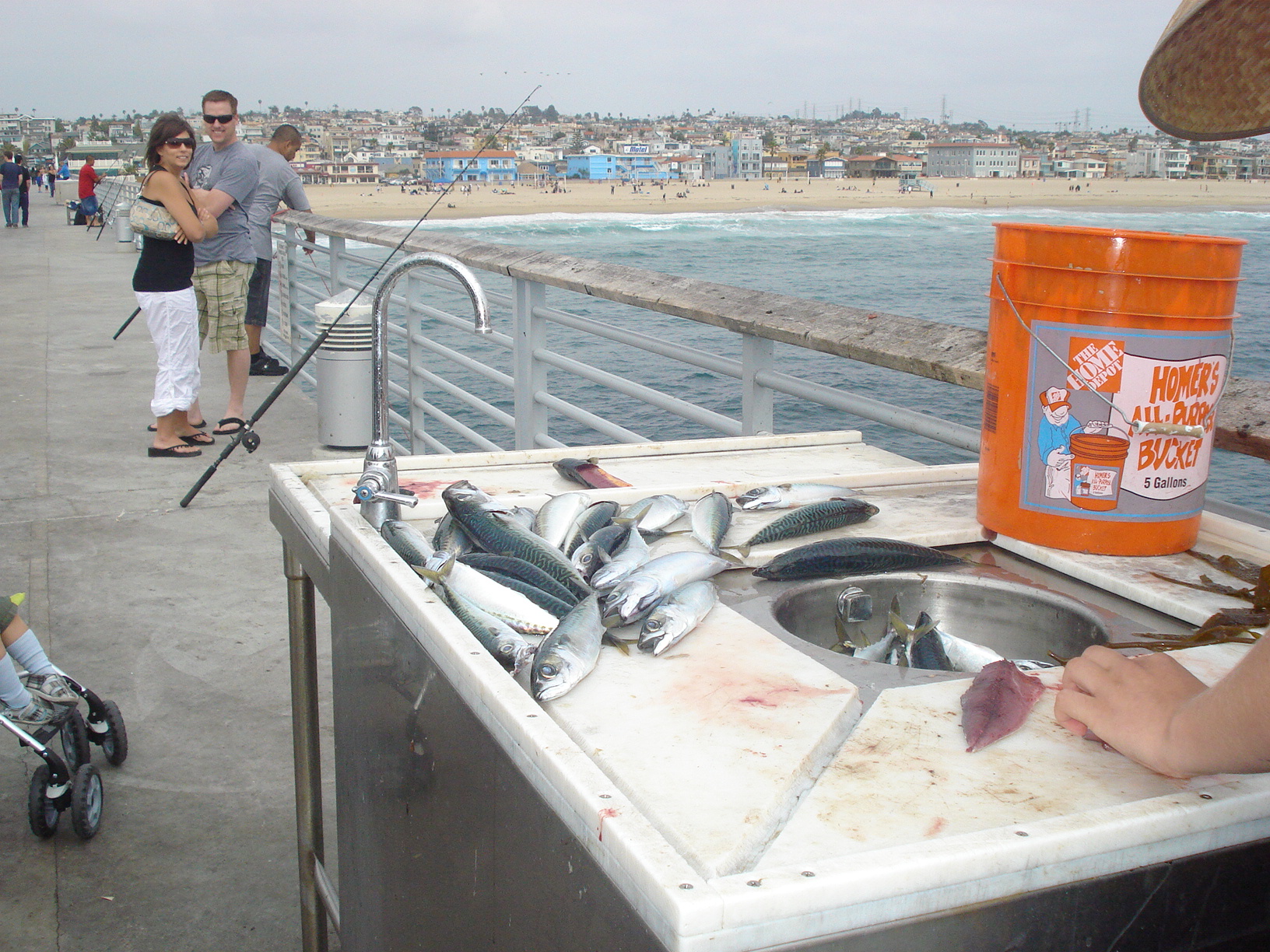
Belmont Pier es popular para pescar y, al igual que otros muelles, no se requiere una licencia de pesca para pescar allí. Sin embargo, los pescadores deben asegurarse de seguir las regulaciones de pesca con respecto al tamaño, límites y temporadas para ciertas especies.
Durante los últimos 18 años, el Programa Educacional Pequero de Heal the Bay (AOP, por sus siglas en inglés) ha estado educando a los pescadores en Belmont Pier (y otros 7 muelles) sobre la contaminación de peces, cuales evitar consumir y qué peces son seguros para el consumo. AOP es parte de Fish Contamination Education Collaborative (FCEC), que es administrado por la Agencia de Protección Ambiental de los EE. UU. (EPA) como parte de un programa de divulgación y educación pública de gran alcance sobre el sitio Superfund de Palos Verdes Shelf.
El muelle de Belmont está ubicado en la zona roja, donde los niveles de DDT y PCB son altos debido a la cercanía con el sitio contaminado. Estas toxinas pueden viajar a través de la cadena alimentacia y acumularse en ciertos peces. Los peces capturados en la zona roja que no deben consumirse son la corvineta blanca, corvineta negra, cabrilla, pejerrey y barracuda.
Nuestro Programa Educacional de Pesca está actualmente suspendido debido a COVID-19, pero cuando estuvimos presente, el muelle de Belmont fue regularmente uno de nuestros principales muelles en términos de cantidad de pescadores. En 2018, llegamos a 9.801 pescadores en 8 muelles en la región de Los Ángeles; Los miembros del equipo de AOP visitaron todos los muelles durante la misma cantidad de tiempo, pero hablaron con más de 2.500 pescadores solo en Belmont Pier (aproximadamente el 25%).
Cuando llevamos a cabo actividades de divulgación con los pescadores, también recopilamos datos sobre los tipos de peces que capturan y códigos postales de dónde residen. En el 2018, recopilamos códigos postales de 1,165 pescadores en Belmont Pier. Los códigos postales de donde provenían la mayoría de los pescadores incluían Long Beach, así como las áreas circundantes de Carson, Bellflower, Paramount y Huntington Park. La recopilación de estos datos ayudan a garantizar que la divulgación también se lleve a cabo en las comunidades donde viven los pescadores, a través de nuestros socios de FCEC.
En el 2018, documentamos que los pescadores en Belmont Pier capturaron 1,051 peces (durante un tiempo total de encuesta de aproximadamente 144 horas). De esos peces, la mayoría (85%) eran macarelas. Descubrimos también que 61 (o el 6%) de esos peces estaban en la lista de “no consumir”, incluida la corvineta blanca, pejerrey y cabrilla. Es necesario continuar educando a los pescadores sobre la contaminación de peces y asegurarse de que tengan los conocimientos necesarios para protegerse a sí mismos y a sus familias.